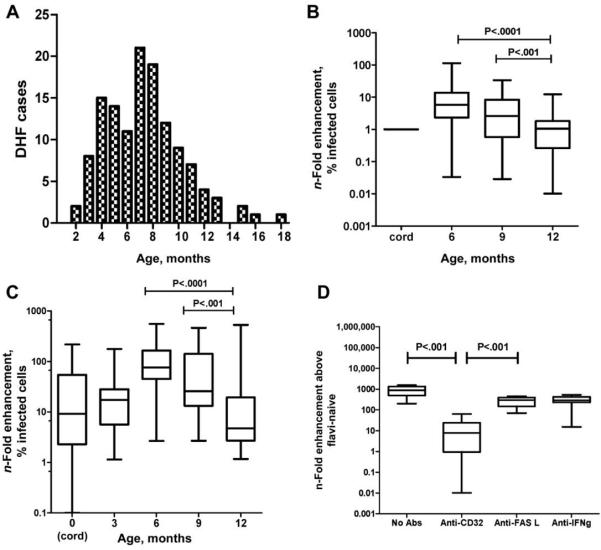
Figure 2.
A, Age-related case prevalence of dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHF) in infants (n = 73) enrolled in a prospective study at Children’s Hospitals 1 and 2 in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, between November 2004 and March 2006. The median age of the infants was 7 months. B, Serial neat plasma samples collected, at birth and at 6, 9 and 12 months of age, from 42 healthy Vietnamese infants born to dengue-immune mothers, and then mixed with DENV2 and cultured with K562 cells for 3 days. Shown is the n-fold increase (median, interquartile, and maximum/minimum range) in DENV2-infected K562 cells in infants’ plasma samples at 6, 9 and 12 months, compared with that in the infant’s own cord-plasma sample. Plasma from 6-month-old infants provided significantly more enhancement than did plasma collected at any other time point (P < .001, by paired t test). C, Individual neat plasma samples collected, at birth and at 3, 6, 9 and 12 months of age, from 150 unrelated healthy Vietnamese infants (n = 30 at each time point), and then mixed with DENV2 and cultured with K562 cells for 3 days. Shown is the n-fold increase (median, interquartile, and maximum/minimum range) in DENV2-infected K562 cells in infants’ plasma samples, compared with that in flavivirus-naive control samples. Plasma from 6-month-old infants provided significantly more enhancement than did plasma collected at any other time point (P < .001, by Mann-Whitney test). D, n-Fold infection enhancement obtained when DENV2 and K562 cells were cultured in the presence of both plasma from 10 6-month-old infants and either monoclonal antibody (mAb) to CD32 (FcγIIa) or 1 of 2 different control mAbs (i.e., anti-FASL and anti-interferon [IFN]-γ). Anti-CD32 mAb significantly abrogated infection enhancement, compared with the control mAbs or no mAb (P < .001, by Mann-Whitney test).