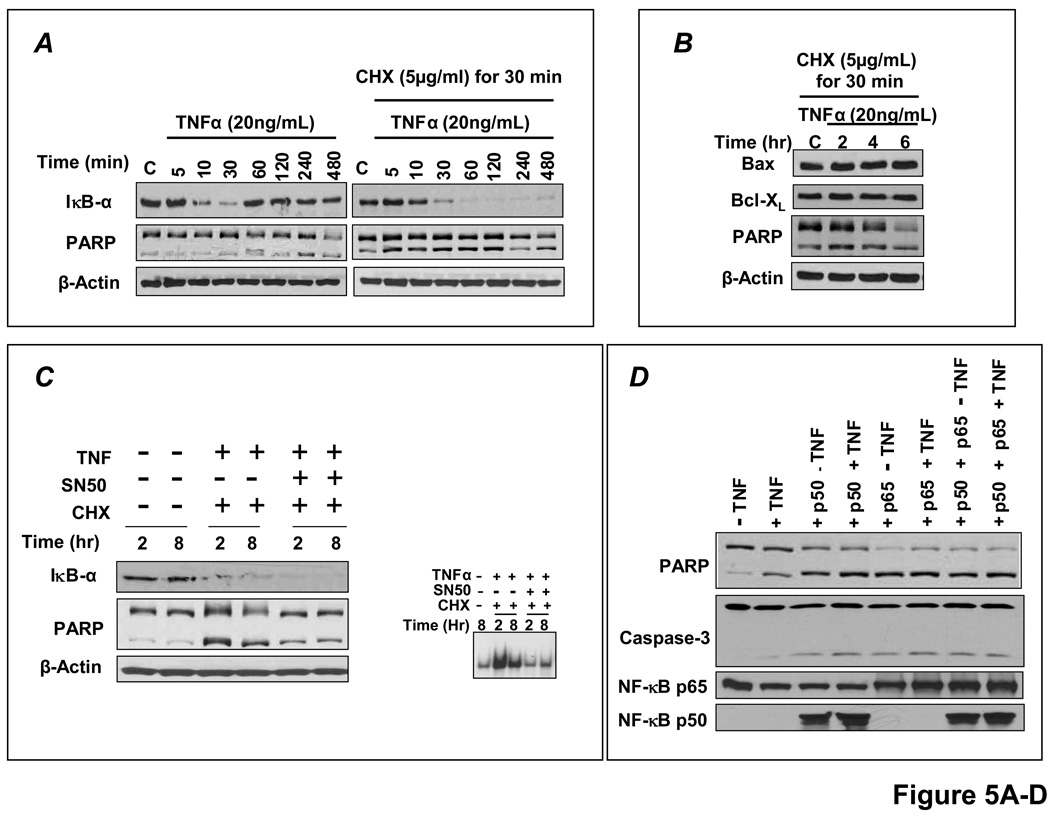
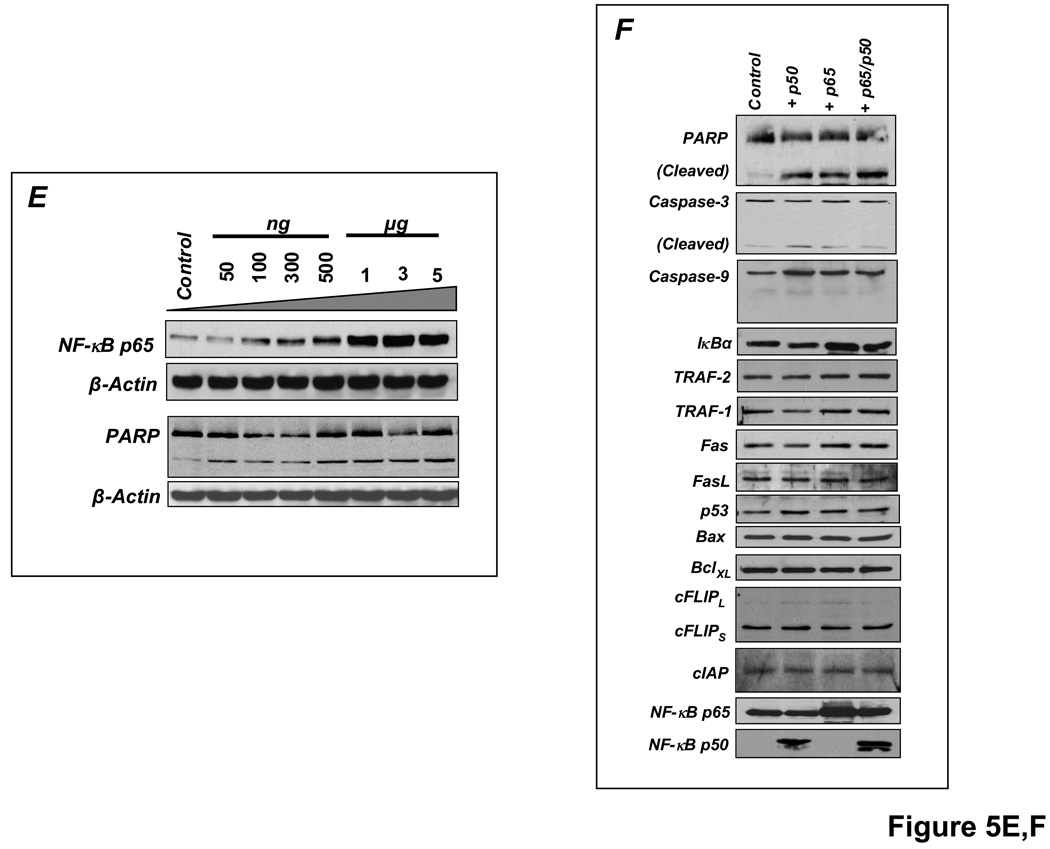
Figure 5.
Sustained NF-κB activation is pro-apoptotic in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. (A) H9c2 cells were treated with TNF with or without pretreatment with the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide (CHX) and cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting. TNF induced rapid IκBα degradation with resynthesis within 1 h but no apoptosis as indicated by predominantly uncleaved PARP. CHX pretreatment prevented IκBα resynthesis and induced apoptosis (augmented cleaved PARP). (B) Bcl-XL protein expression and the Bcl-XL/Bax ratio with CHX pretreatment and TNF stimulation. (C) Pre-incubation with SN50, a peptide inhibitor of NF-κB nuclear translocation, attenuated apoptosis. (D) H9c2 cells were transfected with either empty vector (pcDNA 3.1) or p65 and/or p50 expression vectors for 24 h followed by treatment with or without TNF for 8 h. Sustained p65 or p50 overexpression augmented PARP and caspase-3 cleavage, irrespective of TNF exposure. (E) H9c2 cells were transfected for 24 h with increasing amounts of p65 expression vector and total amount of DNA was compensated with pcDNA3.1. The apoptotic effect of p65 exhibited dose-dependency. (F) H9c2 cells transfected with p65 and/or p50 for 24 h did not exhibit changes in expression of a variety of pro-and anti-apoptotic proteins including TRAF-1 and 2, Fas and FasL, Bax and Bcl-XL, cFLIP and cIAP, and p53. Results in A–F are representative of four independent experiments.