Fig. 1.
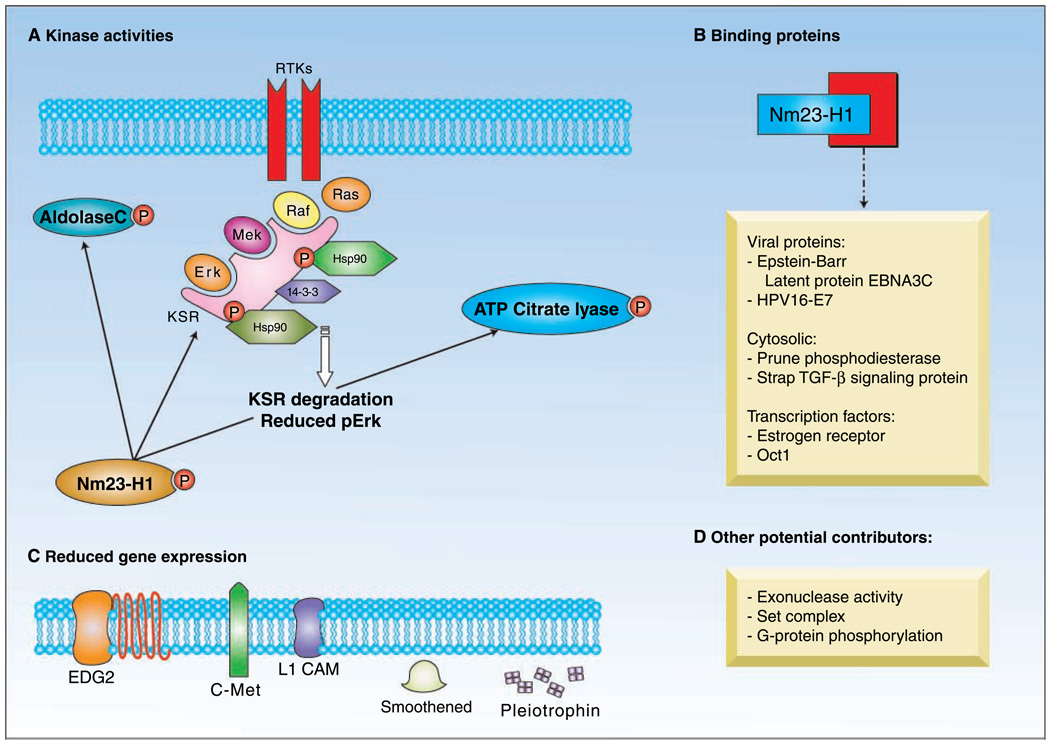
Nm23-H1suppression of tumor metastasis may depend on at least three pathways. A, Nm23-H1is a histidine protein kinase; its substrates include aldolase C, ATP-citrate lyase, and the Ksr, which is a scaffold for the MAP kinase pathway. Differential expression levels of Nm23-H1 result in altered binding of Hsp90 to Ksr, which leads to changes in its degradation and, consequently, ERK activation. B, binding proteins can titrate out free Nm23-H1, resulting in the loss of suppressive capacity.Viral proteins, the Pn protein, transcription factors, and TGF-β signaling intermediates bind Nm23-H1. C, a number of cell surface receptors and growth factors are up-regulated in expression as Nm23-H1is down-regulated. Of these, the receptor for serum LPA, EDG2, is capable of overcoming the Nm23-H1inhibition of both motility in vitro and metastasis in vivo. D, other activities for Nm23-H1 include a DNA exonuclease activity and a member of the set complex, which may potentially contribute to antimetastatic function. Ksr, kinase suppressor of ras; MAP, mitogen-activated protein; Hsp, heat shock protein; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; Pn, prune; TGF, transforming growth factor; LPA, lysophosphatidic acid.