Fig. 2.
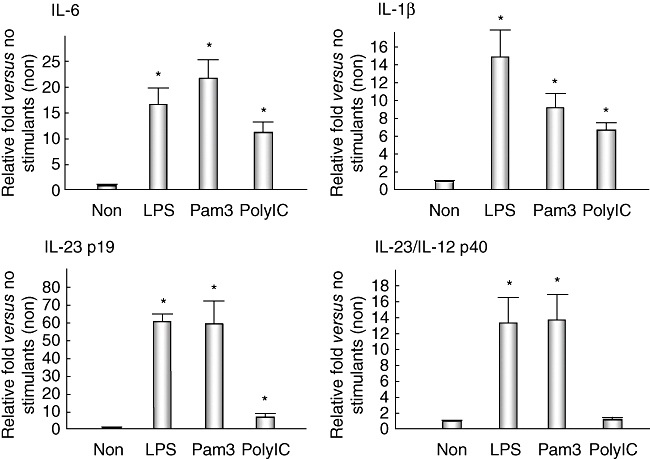
Quantitative analysis of T helper 17 (Th17)-inducible cytokines [interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-1β] and Th17-maintaining cytokines (IL-23 p19 and IL-23/IL-12 p40) in cultured human biliary epithelial cells (BECs). Expression of IL-6 mRNA was up-regulated 16·6 ± 4·3 [mean ± standard error of the mean (s.e.m.)]-fold by stimulation with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) [Toll-like receptor (TLR)-4 ligand], 21·7 ± 2·5-fold with Pam3CSK4 (TLR-1/2 ligand) and 11·3 ± 1·5-fold with poly(I:C) (TLR-3 ligand). The relative fold-increase in the expression of IL-1β caused by LPS, Pam3CSK4 and poly(I:C), compared with no stimulant (non), was 14·9 ± 4·1, 9·2 ± 1·6 and 6·7 ± 0·6, respectively; that of IL-23 p19 was 60·7 ± 3·0, 60·0 ± 15·7 and 7·3 ± 0·6, and that of IL-23/IL-12 p40 was 13·4 ± 3·3, 13·7 ± 3·6 and 1·2 ± 0·3, respectively. LPS and Pam3CSK4 up-regulated the production of all these cytokines significantly (P < 0·05). Poly(I:C) also up-regulated the production of IL-6, IL-1β and IL-23 p19 (P < 0·05), but not IL-23/IL-12 p40. Duplicate experiments were performed using three lines of cultured biliary epithelial cells (BECs) (BEC1–BEC3) and data are shown as the mean ± s.e.m.
