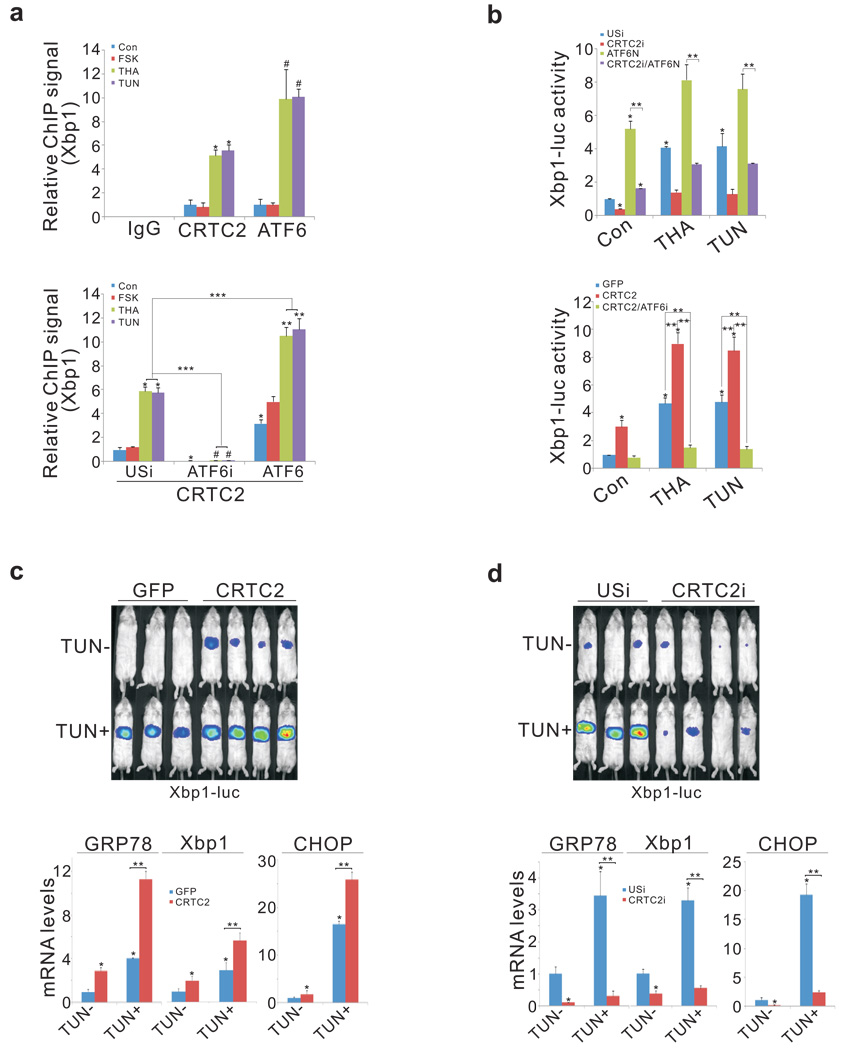
Figure 2.
CRTC2 stimulates the expression of ER quality control genes through an association with ATF6α. A. Top, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay showing occupancy of CRTC2 and ATF6α over the Xbp1 promoter in primary hepatocytes exposed to THA or TUN. Bottom, effect of adenoviral ATF6α over-expression or RNAi mediated knockdown (ATF6i) on CRTC2 occupancy. (P* < 0.01; P# < 0.01; P** <0.01; P***< 0.001; n=3) B. Top, effect of adenoviral ATF6N on Ad-Xbp1 luc reporter activity in control (USi) and CRTC2-depleted (CRTC2i) cells. Bottom, effect of Ad-CRTC2 on Ad-Xbp1 luc reporter activity in control and ATF6α-depleted hepatocytes. (P* < 0.01; P** < 0.01; n=4). C. and D. Top, hepatic Ad-Xbp1 luc reporter activity in mice injected intraperitoneally (IP) with TUN or vehicle. Effect of Ad-CRTC2 over-expression (C) or Ad-CRTC2 RNAi (D) on Ad-Xbp1 luc activity (top) and on hepatic mRNA amounts for ATF6α-regulated genes (P* < 0.01; P** < 0.01; n=4).