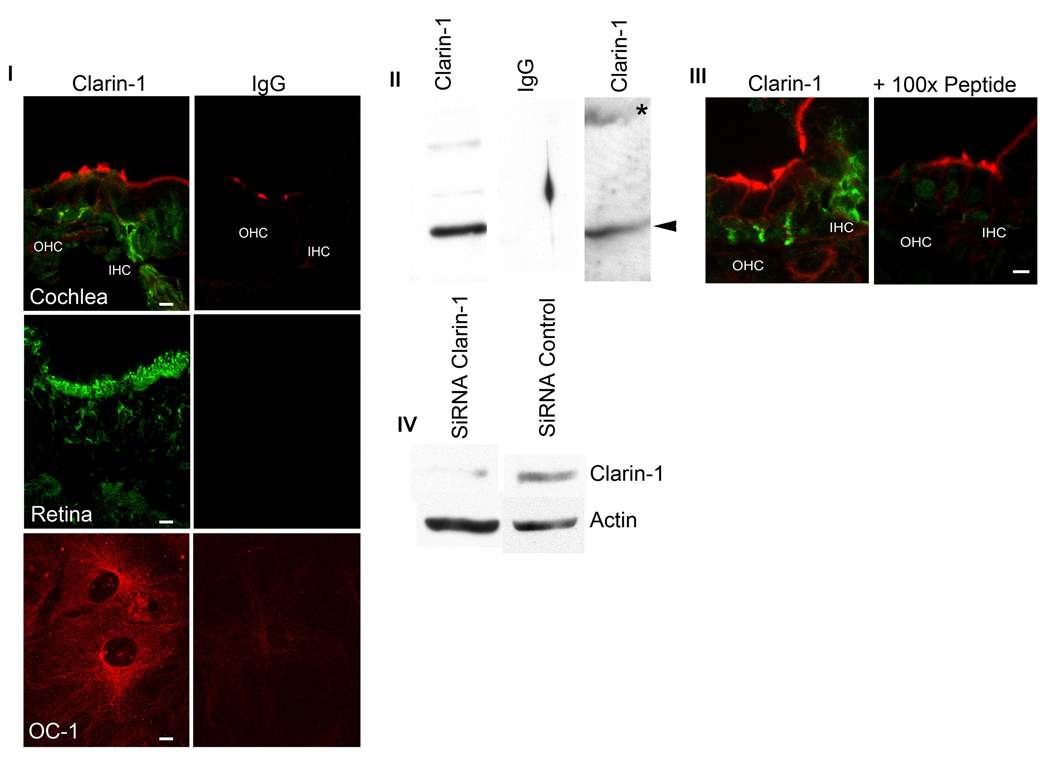
Figure 2.
Anti-clarin-1 antibody qualification. Panel I: P3 mid-modiolar cross sections, P28 eye and differentiated UB/OC-1 cells were incubated with anti-clarin-1 antibody or normal rabbit IgG and analyzed by fluorescence confocal microscopy (see Materials and Methods). Panel II: Western blot analysis of P3 cochlea (lane 1 and 2) and UB/OC-1 cells (lane 3) transfected with GFP-clarin-1 fusion protein. Membranes were probed with anti-clarin-1 antibody (lane 1 and 3) or normal rabbit IgG (lane 2). Arrowheads denote endogenous clarin-1. Asterisk denotes GFP-clarin-1 fusion protein. Panel III: Confocal microscopy of P3 mid-modiolar sections incubated with anti-clarin-1 antibody alone or in the presence of 100-fold molar excess the fusion protein used to generate the antibody. Panel IV: Western blot analysis of UB/OC-1 cells transfected with a siRNA specific for clarin-1 (lane 1) or an unrelated siRNA (lane 2). The membrane was cut in half and probed with either anti-clarin-1 or with anti-β-actin antibodies, as loading control (bottom).