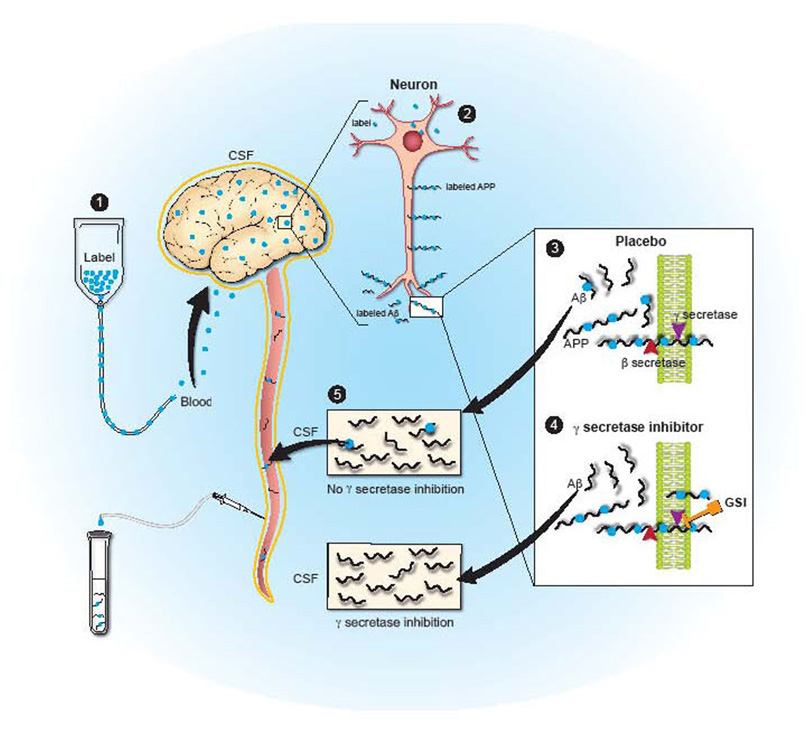
Figure 1. Diagram of Central Nervous System Stable Isotope Labeled Kinetics (CNS-SILK).
1) A stable isotope labeled amino acid is infused into the blood stream and is transported to the brain. 2) The labeled amino acid is incorporated into newly synthesized proteins (e.g. APP in neurons). 3) Labeled APP is cut by β- and γ-secretases to produced labeled Aβ, or in the presence of a gamma-secretase inhibitor (4) labeled Aβ production is inhibited. 5) Labeled and unlabeled Aβ is transported and cleared through the cerebral-spinal fluid which is in direct communication with the extracellular space of the brain, where sampling occurs over time to measure the production and clearance of Aβ.