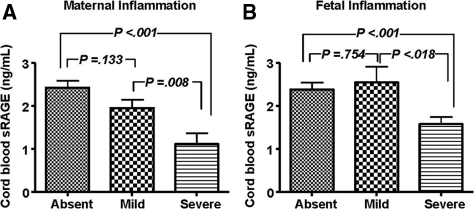
Figure 1.
Relationship between histological evidence of maternal (A) or fetal (B) inflammation and umbilical cord blood levels of soluble RAGE (sRAGE). sRAGE was measured using an immunoassay (R&D Systems) that detects a heterogeneous population of soluble RAGE proteins that encompass both alternative splice variants and cleavage forms of RAGE. Maternal inflammation was assessed by the extent of inflammatory infiltration of the amnion as absent (n = 59), mild (n = 29), or severe (n = 33), as described in Materials and Methods. The extent of inflammatory infiltrate in umbilical cord and/or chorionic vessels was used to establish the level of fetal inflammation as either absent (n = 43), mild (n = 14), or severe (n = 64). One-way analysis of variance followed by posthoc Student-Newman-Keuls tests was used for statistical analysis. Error bars indicate SE.