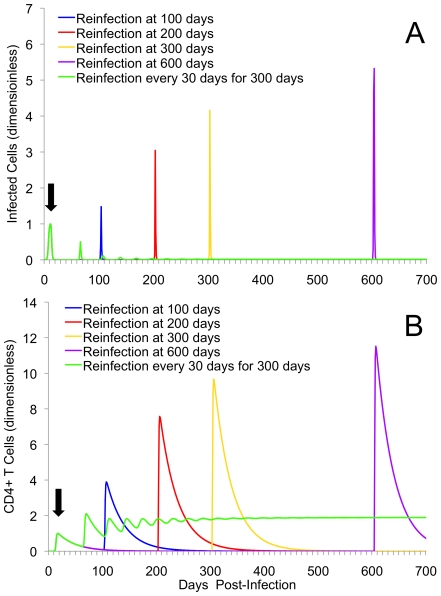
Figure 4. Multiple re-exposure experiments using the basic model.
Displayed are the kinetics of infected cells (A), and CD4+ T cells (B) for single reinfection at either 100, 200, 300, or 600 days after initial infection in the basic model. Also included is the simulated kinetics of frequent re-exposure every 30 days over a span of 300 days after initial infection. As time of second infection occurs at increasingly long intervals from initial infection, the magnitude of infection and immune responses increases. For frequent re-exposure, it should be noted that oscillatory behavior continued after the removal of further infection. Single and multiple re-exposure scenarios are used to represent individuals that have low and high sexual exposure to chlamydia, respectively. Black arrow indicates point of initial infection (common to all scenarios). The magnitude and time evolution of the system of equations in both (A) and (B) are presented non-dimensionally.