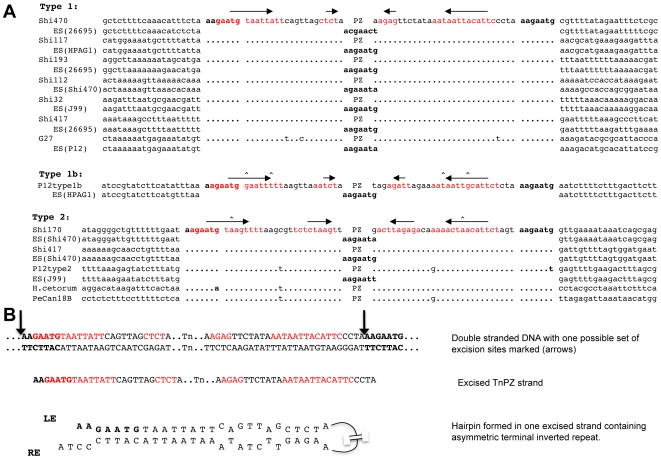
Figure 2. TnPZ flanking sequences, termini, insertion sites and corresponding empty sites.
A. Alignments of sequences at multiple sites of insertion. A seven bp target (5′AAGAATG or closely related sequence) is present as direct repeats at each TnPZ end, and in single copy at unoccupied (empty) sites. Inverted repeats that could form foldback (hairpin) structures in single stranded DNA are marked in red and underlined, with their orientation shown by arrows. Corresponding empty site (ES) locations were chosen from strains with the highest sequence matches. TnPZs and remnants from strains 26695, J99 and HUP-B43 were not included due to their chimeric nature and rearrangements. The sequence from strain PeCan18B includes only its type 2 TnPZ (type 1b remnant is missing several hundred bp at its normal TnPZ end, including its 5′AAGAATG target). No corresponding empty site for PeCan18B was found; this we ascribe to the variable and repetitive nature of sequences in the 5S,23S rRNA - ftsZ interval (Fig. S9). Type 1 TnPZ insertion sites: Shi470 and five other Shimaa strains, in hp0488; Shi117, in gene HPAG1_0627 (frxA, encodes NAD(P)H-flavin oxidoreductase); Shi193 and 17 other Shimaa strains, in intergenic region between hp0209 and hp0210; Shi112 and eight other Shimaa strains, in intergenic region between HPSH_07175 and the rRNA gene HPSH_r08356 (equivalent to jhp1299 – 5S,23S rRNA interval of J99); strain Shi32, in jhp0244 (methyltransferase of type II restriction modification system); strain Shi417, between hp1159 and hp1160; strain G27, between HPP12_1009 and the tRNA gene HPP12_t21. Type 1b TnPZ insertion site: strain P12 in gene HPAG1_0439 (encodes type I restriction-modification R protein (hsdR)). Type 2 TnPZ insertion sites: Shi170 and seven other Shimaa strains, between HPSH_01160 and HPSH_01165 (jhp0210 and jhp0211 in strain J99); strain Shi417, in HPSH_07895 (encodes type I restriction modification R protein (hsdR)) of strain Shi470 (equivalent to jhp1424 of strain J99); strain P12 (type 2), in jhp1272; H.cetorum, no counterpart for this insertion site in H. pylori genome sequences; strain PeCan18B type 2, between the 5S,23S rRNA gene pair and ftsZ (jhp0913). B. Hairpin structures involving TnPZ termini. This illustrates a hypothetical excision of one TnPZ strand, a possible product of TnPZ transfer from strain Shi470 to recipient cells. The sites of single strand cleavage (arrows) are also placed arbitrarily, to maximize hairpin length and to cut at the ends, rather than within, the heptanucleotide target sequences. The third line illustrates the type of foldback (hairpin structure) that would be formed by annealing of complementary sequences from terminal inverted repeats. An equivalent structure would be formed by excision of the other DNA strand.