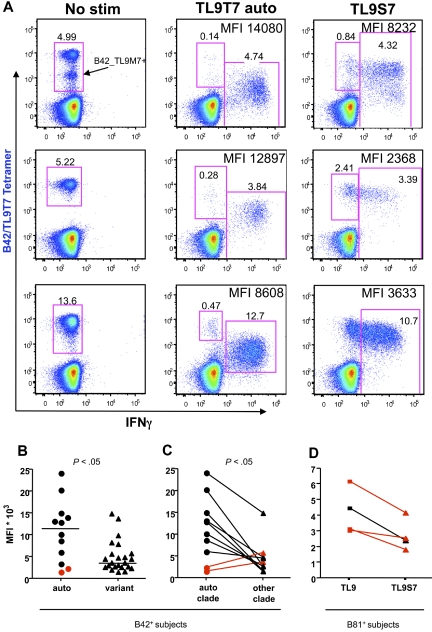
Figure 3.
TL9 epitope variant recognition is associated with reduced IFN-γ production and attenuated TCR down-regulation. (A) Representative CD8 T cell–gated dot plots from subtype C–infected B42+ subjects (from top to bottom, H325, H234, H122) showing TL9T7/B42 tetramer staining (y-axis) versus intracellular IFN-γ production (x-axis) after stimulation with TL9T7 or the TL9S7 variant; the MFI of IFN-γ+ cells is indicated. The intermediate tetramer-positive population indicated in the top left panel is a cross-reactive population that also binds the TL9M7/B42 tetramer. (B) Comparison of IFN-γ MFI values in B42+ samples stimulated with autologous peptide or different TL9 variant peptides. Horizontal bars represent median values. (C) Comparison of IFN-γ MFI values in B42+ samples stimulated with autologous or nonautologous subtype-specific peptides. Two subjects with an “escaped” autologous mutant epitope (TL9T3) are highlighted in red. (D) Comparison of IFN-γ MFI values in B81+ samples infected with subtype C stimulated with the subtype C consensus TL9T7 or with the variant peptide TL9S7. Three subjects with an autologous TL9S7 mutant epitope are highlighted in red. Statistical analysis was performed using the 2-tailed Mann-Whitney test (B) or the 2-tailed Wilcoxon test (C).