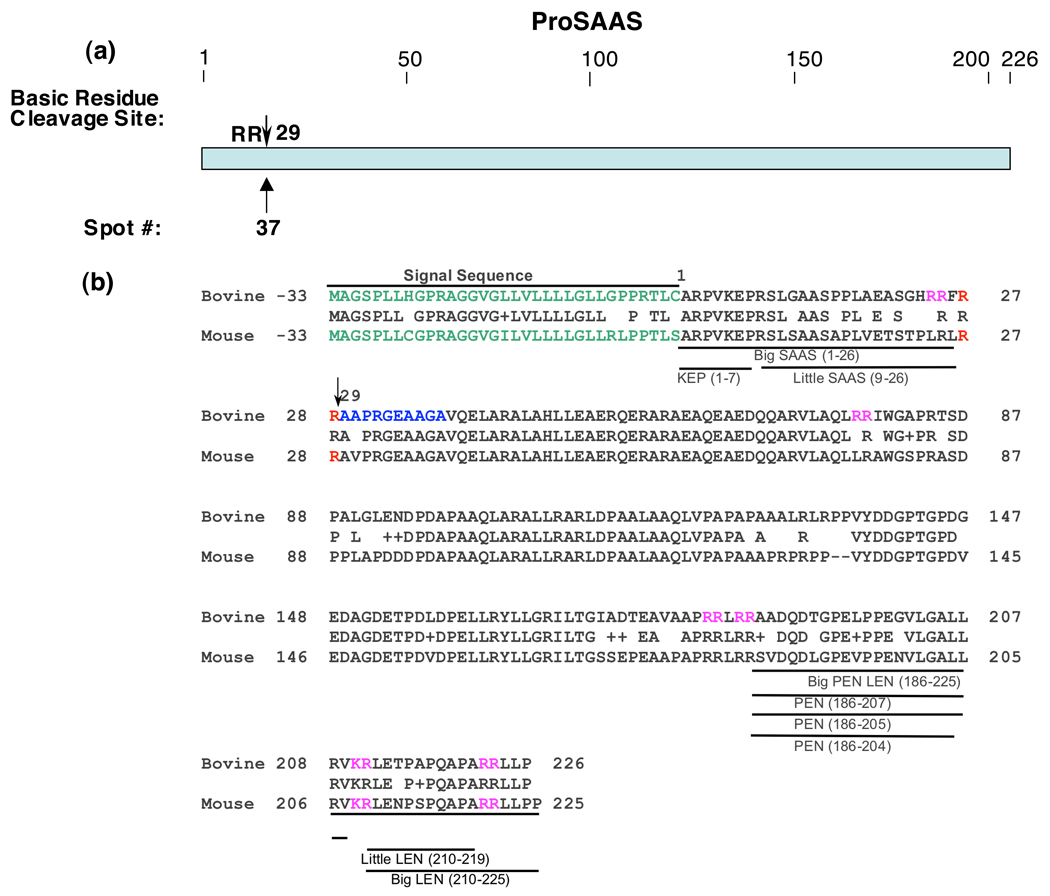
Figure 4. Cleavage site of proSAAS proteolytic fragment.
a. NH2-terminal cleavage site of proSAAS fragment. The Arg-Arg cleavage site utilized to generate the proSAAS fragment isolated by 2-D gels of chromaffin granules is illustrated by the arrow.
b. ProSAAS-derived peptides and cleavage sites. The arrow at residue #29 indicates the cleavage site of proSAAS determined by NH2-terminal Edman sequencing from its protein spot obtained from the 2-D gel (figure 1). The bovine sequence for proSAAS is aligned with the mouse proSAAS sequence, with active mouse peptides indicated. Since proSAAS-derived peptides have been characterized in mouse tissues (rather than bovine tissues), the proSAAS peptide fragments are shown for mouse proSAAS (NCBI Protein Database accession number Q9QXV0 (39–41)) and aligned to the bovine proSAAS sequence (accession number NP001077149 ).