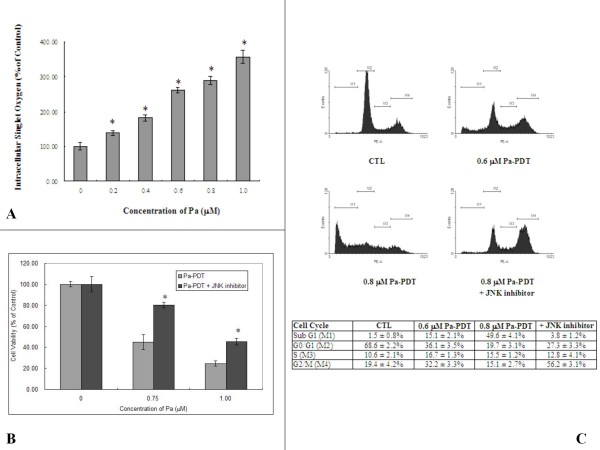
Figure 3.
Pa-PDT triggers JNK-dependent apoptotic pathway in R-HepG2 cells. (A) Intracellular singlet oxygen generation. Cells (2 × 104/well) were treated with various concentrations of Pa-PDT, then the treated cells were stained with 10 μM trans-1-(2'-methoxyvinyl) pyrene at 10 min after the PDT for 15 min in dark. The intensity of fluorescence was detected with a plate reader; the results shown are representative as mean ± S.D. of 3 independent experiments (* p value < 0.005). (B) Involvement of JNK in the Pa-PDT induced cell death pathway. Cells (1 × 104/well) were co-incubated with increasing concentrations of Pa and 0.5 μM JNK inhibitor in a 96-well plate for 2 h and then treated with PDT, and subsequently incubated at 37°C, 5% CO2. Cell viability was then assessed by MTT assay 24 h after treatment. Results are mean ± SD of three experiments (* p value < 0.005). (C) For cell cycle analysis, cells with Pa or co-incubated with 0.6 μM Pa and 0.5 μM JNK inhibitor were harvested at 24 h after PDT treatment, fixed and stained with PI (10 μg/ml, 30 min). The stained cells were analyzed by flow cytometry, and the percentage of cell population in subG1, G0/G1, S and G2/M phase were shown in the table as mean ± SD of three independent experiments.