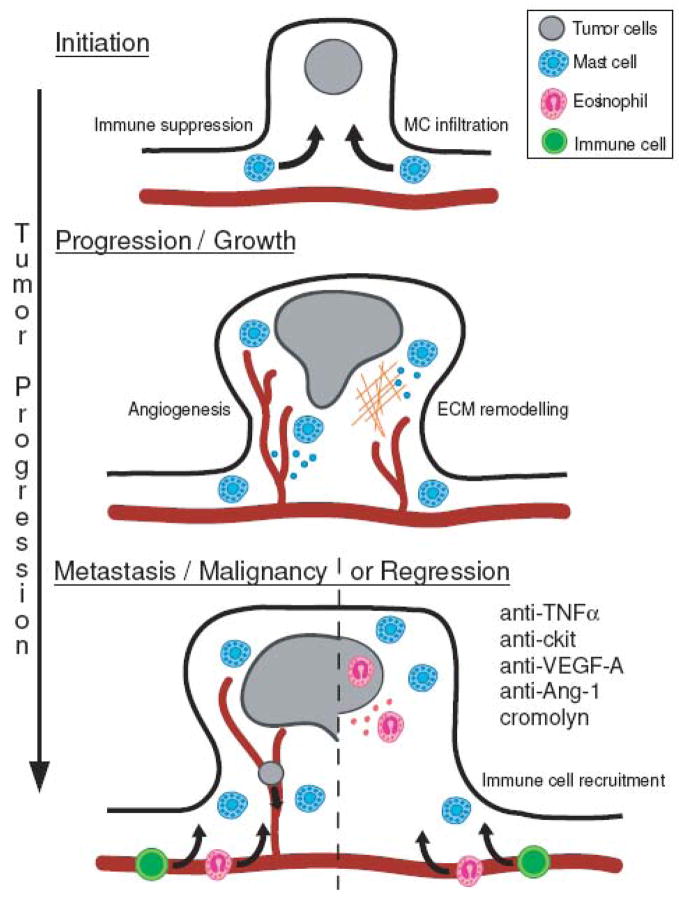
Figure 2. Schematic representation of mast cell functions at different stages in tumor progression, using colon polyp formation as an example.
Mast cell infiltration occurs rapidly following tumor initiation. Mast cells accumulate at the boundary between healthy tissue and the tumor and early in tumor growth mast cells play an active role in promoting angiogenesis and tissue remodeling. At later stages, mast cells induce immune suppression, promoting tumor growth or alternatively, recruitment of mature immune effector cells, leading to rejection. Interventions with antibodies recognizing TNFα c-kit, VEGF-A or Ang-1 or the chemical cromolyn induce regression, by blocking mast cell maintenance of the tumor.