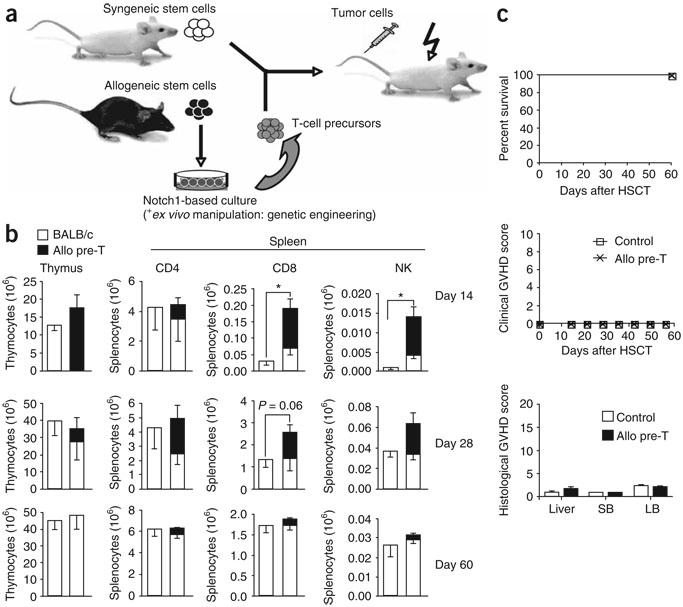
Figure 1.
Adoptively transferred allogeneic T-cell precursors enhance T and NK cell reconstitution and do not induce GVHD. (a) Lethally irradiated BALB/c mice were transplanted with syngeneic purified HS cells (or lin− bone marrow cells); control mice received HS cells only, the treatment group received additional T-cell precursors generated in OP9-DL1 cocultures. In some cases, transplantation recipients were intravenously challenged with tumor cells to study anti-tumor activity. allo, allogeneic. (b) Lethally irradiated BALB/c recipients were transplanted with BALB/c mouse HS cells (Ly9.1); control mice received HS cells only, the treatment group received additional C57BL/6-derived in vitro–generated T-cell precursors (CD45.1+). At days 14, 28 and 60 after HSCT, animals were killed and thymi and spleens were harvested. Origin of cells, whether from BALB/c or C57BL/6 mice, was determined by total cellularity and multicolor flow cytometric analysis using Ly9.1- and CD45.1-specific antibodies. T and NK cells were analyzed using antibodies to CD3, CD4, and CD8, and DX5, respectively. Combined data of more than three independent experiments are presented. Values represent mean cell numbers and s.e.m. (n = 5–10). *, P < 0.05. (c) Lethally irradiated BALB/c recipients were transplanted with lin− BALB/c mouse bone marrow; control mice received bone marrow only, the treatment group received additional C57BL/6 T-cell precursors. Survival was monitored daily, a clinical GVHD score was monitored weekly. Histopathological analysis of signs of subclinical GVHD in liver, small bowel and large bowel was performed 8 weeks after transplantation. Data are representative of more than three independent experiments. Mean values and s.e.m. are presented (n = 5).