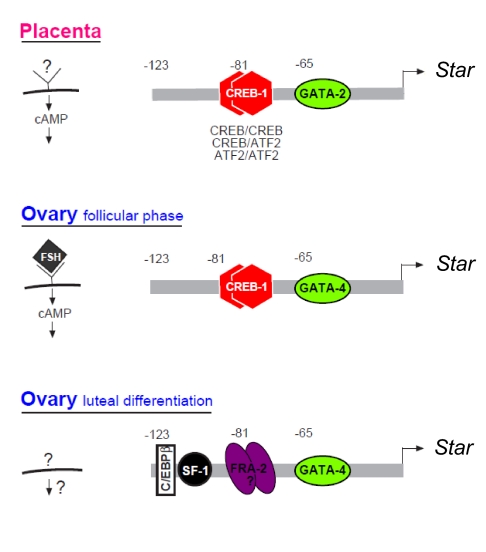
Figure 10.
Tissue-specific modes of Star regulation in the placenta and the ovary schematic representation. Upper panel, In placental cells, cAMP up-regulates transcription requiring binding of GATA-2 (−66/−61), as well trans-factor dimers that bind a CRE half-site defined as CRE2 (−81/−78). CRE2 binds CREB homodimers, ATF-2 homodimers, and CREB-ATF-2 heterodimers. Middle and lower panels, The ovarian mode of Star regulation distinguishes between FSH/cAMP responsive granulosa cells in the follicular phase (i.e. before LH-induced luteinization), and after LH surge terminally differentiated luteal cells when Star expression becomes cAMP independent. As shown, regulation of Star in FSH/cAMP responsive cells is similar to the placental pattern, but for GATA-4 that is predominantly expressed in the ovary, instead of the placental GATA-2 isoform. Bottom panel, In hormone-independent luteal cells, Star transcription requires additional factors interacting at the promoter, including GATA-4, FRA-2 (a dimmer with a yet unknown partner) that substitutes CREB binding to the −81/−78 site, and upstream binding of C/EBPβ (−117/−108) and SF-1 (−102/−95).