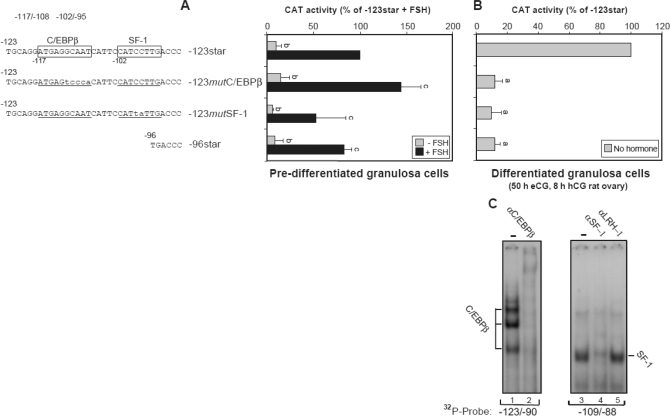
Figure 9.
Involvement of C/EBPβ and SF-1 in activation of the Star promoter in luteinizing granulosa cells, through binding to their upstream C/EBPβ-1 and SF-1 elements. A, Predifferentiated granulosa cells were transfected by electroporation with CAT plasmids controlled by −123Star, −96Star, or a −123Star promoter mutated in the C/EBPβ-1 (−123mutC/EBPβ-1) or SF-1 site (−123mutSF1). Four hours after seeding, the cells were treated with 100 ng/ml FSH for 6 h, and cell extracts were prepared. CAT activity was determined using 5 μg protein for a 1-h assay. Activity values (mean ± sd) are presented relative to the activity of −123Star treated with FSH and were statistically significant when compared with the −123Star activity; b, P < 0.05; c, P > 0.1. B, Luteinizing granulosa cells from eCG/hCG treated rats were transfected by electroporation with −123Star-CAT, −123mutC/EBPβ-1, −123mutSF1a, or the −96Star plasmid. CAT activity was determined using 20 μg protein for a 7-h assay. Activity values (mean ± sd) are presented relative to the activity of −123Star and were statistically significant when compared with the −123Star activity; a, P < 0.001. C, EMSA was performed using ovarian extracts from eCG/hCG treated rats. Antiserum to C/EBPβ was preincubated with the protein extract before assay with radiolabeled −123/−90 probe, and antibodies against SF-1 or LRH-1 were incubated with the protein extract before assay with −109/−88 DNA probe.