Fig. 2.
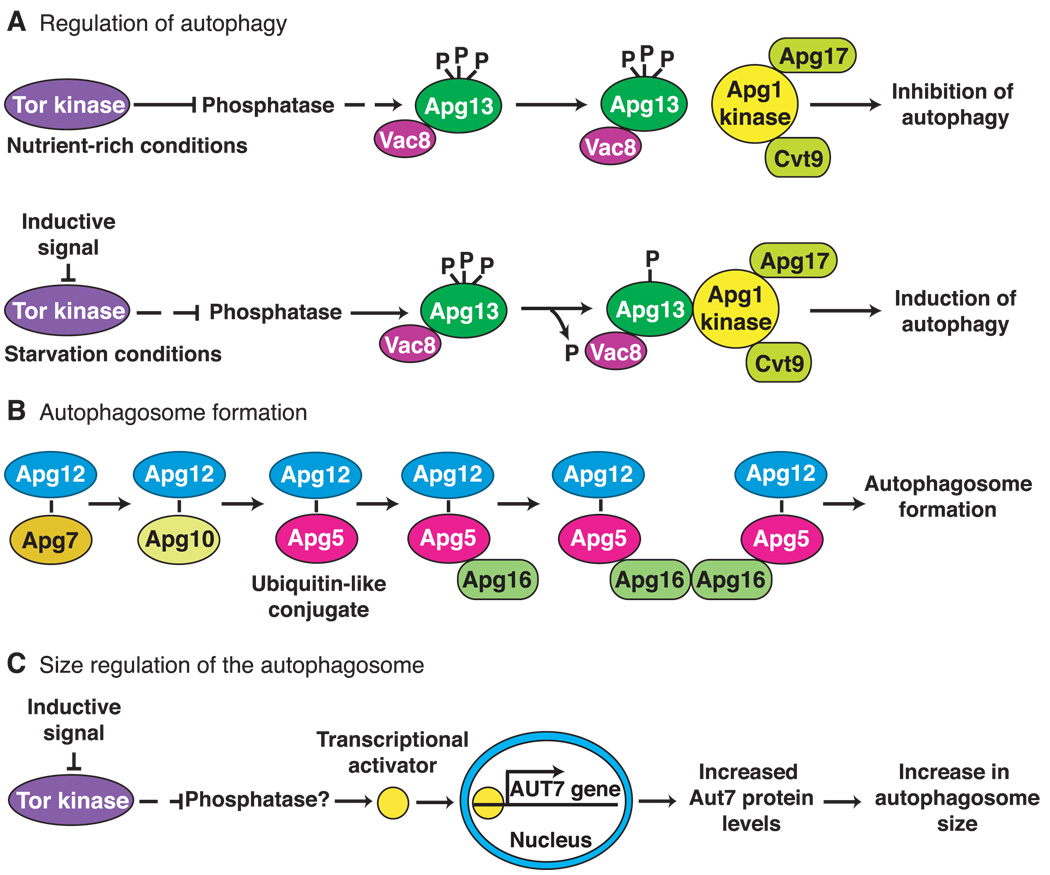
Molecular genetics of macroautophagy in yeast. (A) The Tor kinase exerts a negative regulatory effect on autophagy when cells are growing under nutrient-rich conditions. When starvation occurs, the Tor kinase is inactivated, and the negative regulation is relieved resulting in induction of autophagy. Most of the proteins required for autophagy are constitutively expressed and are used for biosynthetic import through the cytoplasm to vacuole targeting pathway under these conditions. The downstream effectors of Tor are likely to include phosphatases and kinases that modulate the phosphorylation state of Apg13. An inductive signal such as carbon or nitrogen starvation inactivates Tor and results in partial dephosphorylation of Apg13. This form of Apg13 associates more tightly with the Apg1 kinase and stimulates its activity. The function of Apg1 kinase is required for autophagosome formation. (B) The Apg7 (E1-like) and Apg10 proteins form thioester intermediates through a COOH-terminal glycine of Apg12. Apg12 is ultimately conjugated to Apg5 through an internal lysine residue in Apg5 in a process that is similar to ubiquitination. Apg16 binds the conjugated Apg5 protein noncovalently and dimerizes to form a complex that is required for formation and completion of the autophagosome. (C) Under nutrient-rich conditions, the Tor kinase negatively regulates the expression of the AUT7 gene resulting in basal levels of Aut7 synthesis. Under these conditions the Cvt pathway is operative and 150-nm Cvt vesicles are formed. Inhibition of Tor by transduction of an environmental signal or after treatment with rapamycin allows the activation of a presumed transcriptional activator protein that increases expression of AUT7. The resulting increase in Aut7 levels allows an expansion in the size of the autophagosome from 150 nm to a range of 300 to 900 nm.