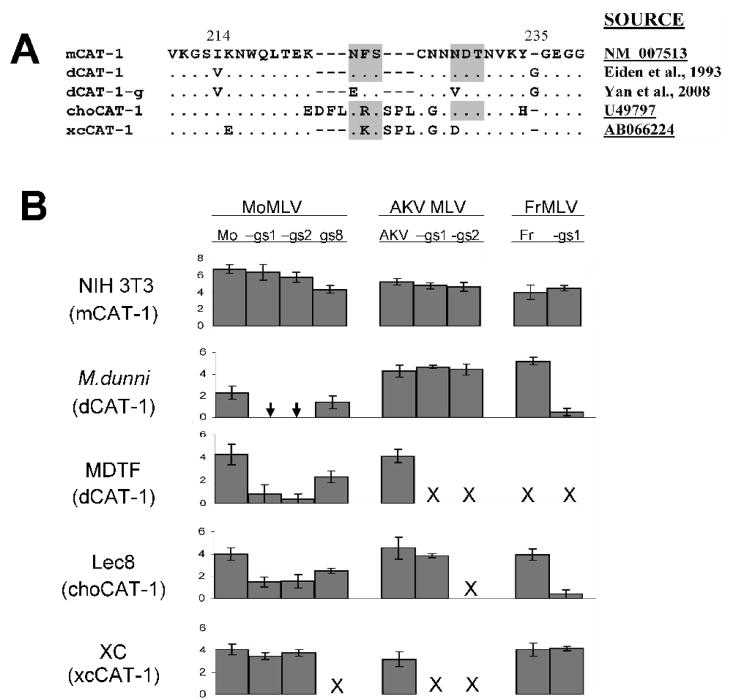
Figure 2.
Infectivity of wild type ecotropic MLVs and mutated viruses that lack specific sites for N-glycans A) Amino acid sequence comparisons of rodent variants of the third extracellular loop of the CAT-1 receptor. mCAT-1 is found in laboratory mouse strains and dCAT-1 is found in the Asian wild mouse species M. terricolor (M. dunni). choCAT-1 and xcCAT-1 are the Chinese hamster and rat XC cell variants. Sites for N-glycosylation are shaded. Glycosylation sites were removed from dCAT-1 to produce dCAT-1-g as described previously (Yan et al., 2008). References or GenBank accession Nos. are provided for each sequence. B) Viruses were tested on 5 cell lines carrying 4 naturally occurring variants of the CAT-1 receptor. Virus titers were determined by the XC overlay test in which the indicated cells were infected with virus dilutions, irradiated and overlaid with XC cells to identify virus infected cells (Rowe et al., 1970; Yan et al., 2008). Virus titers are given as the log10 number of XC PFU in 0.2 ml. Chinese hamster E36 cells were resistant to infection by all viruses (not shown). Results for each set of viruses are from one representative experiment; each set was tested at least 3 times. SD of the data are also shown. Arrow: in 8 trials, XC plaques were produced once for the two viruses, with log10 virus titers of 0.2 for Mo-gs1 and 0.3 for Mo-gs2. X: not done.