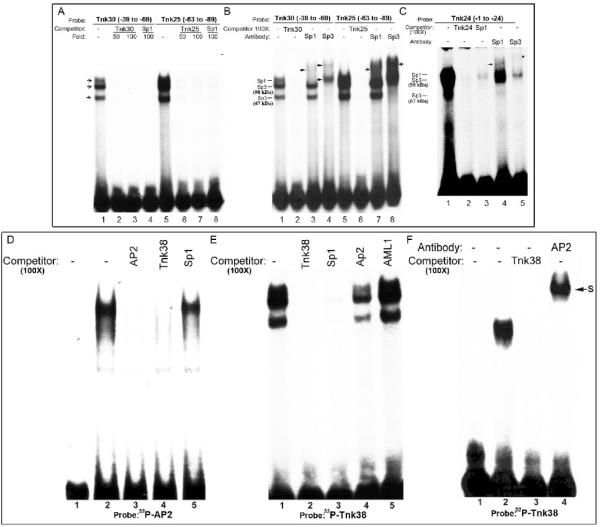
Figure 4. Identification of nuclear proteins that interact with Sp1 and AP2 binding sites in the m-Tnk1 promoter.
Identification of nuclear proteins that bind to GC boxes (A, B and C). EMSA was performed by incubating nuclear extract (10μg) prepared from NIH3T3 cells with 32P labeled Tnk oligonucleotides: Tnk30 (A, lane1; B, lane1), Tnk25 (A, lane5; B, lane5) and Tnk24 (C, lane1). Competition assays were carried out in the presence of 50 or 100 fold molar excess of cold Tnk30 (A, lanes 2, 3; B, lane 2), Tnk25 (A, lanes 6,7; B, lane 6) and Tnk24 (C, lane 2) or Sp1 consensus oligonucleotide (A, lanes 4,8; C, lane3). Super-shift assays were performed using antibodies against Sp1 (B, lanes 3, 7; C, lane 4) and Sp3 (B, lanes 4, 8; C, lane5). Arrows indicate supershifted complexes. Identification of nuclear proteins that bind to the AP2 consensus site (D). Gel shift assay for nuclear proteins prepared from NIH 3T3 that complex with 32P labeled AP2 oligonucleotide (lane 2). The radio-labeled band was competed with 100 fold molar excess of unlabeled AP2 oligonucleotide (lane 3), Tnk38 oligonucleotide (lane 4) or Sp1 oligonucleotide (lane 5). Lane 1 represents reaction mixture without nuclear extract. Identification of nuclear proteins that bind to the AP2/AML1 consensus site (E). The protein DNA complex formed between 32P labeled Tnk38 (-40 to -76) and NIH3T3 nuclear extract (lane1) is tested for competition with 100 fold molar excess of unlabeled oligonucleotides Tnk38 (lane 2), Sp1 (lane 3), AP2 (lane 4) and AML1a (lane 5). AP2 binds the AP2/AML1 consensus site (F). Purified AP2 recombinant protein (50ng) was allowed to react with 32P labeled Tnk38 (lane 2) in the presence of 100 fold molar excess of unlabeled Tnk38 (lane 3) or an antibody for AP2α (lane 4). S indicates the position of the super-shifted complex. Lane 1 shows reaction mixture without protein.