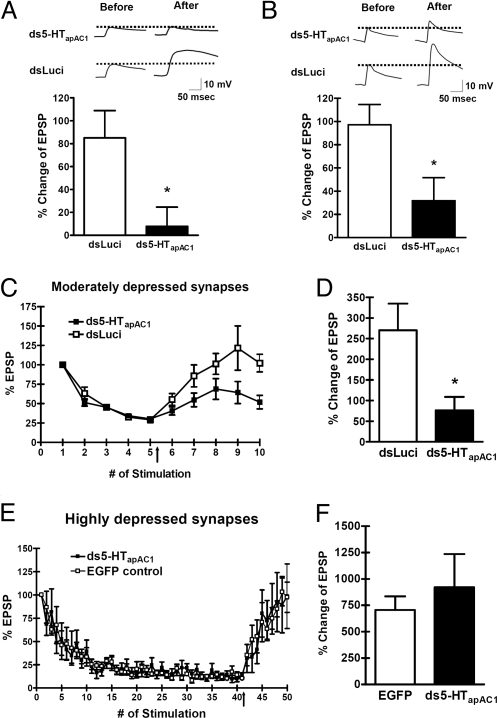
Fig. 6.
Blockage of 5-HTapAC1 expression impaired short-term facilitation in nondepressed and moderately depressed synapses. (A and B) Short-term facilitation induced by 5-HT treatment (10 μM, 1 min) followed by 4 min of wash out (A) or 5-HT treatment (10 μM, 5 min) (B) was significantly reduced both cases in ds5-HTapAC1-injected synapses compared to control synapses. EPSP amplitudes were measured both before and 5 min after 5-HT treatment, and the percent of amplitude change was calculated. (C and D) 5-HT treatment (10 μM, 5 min) reversed a moderate degree of synaptic depression only in control synapses, indicating that cAMP is required for this degree of depression. % Change of EPSP = (mean EPSP at the 9th and 10th stimuli) − (mean EPSP at the 4th and 5th stimuli)/(mean EPSP at the 4th and 5th stimuli) × 100 (%). (E and F) By contrast, 5-HT treatment reversed a high degree of synaptic depression comparably in both dsRNA-injected and control synapses. Percent change of EPSP = (mean EPSP between the 36th and 40th stimuli) − (mean EPSP between the 46th and 50th stimuli)/(mean EPSP between the 46th and 50th stimuli) × 100 (%). Unpaired, two-tailed t test; *, P < 0.05.