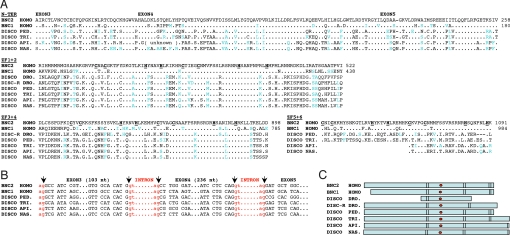
Fig. 6.
Relatedness of basonuclins and disco proteins. (A) Alignment of the N-terminal sequence and of the 3 pairs of zinc fingers of human bnc2 (GenBank NP_060107.3) with those of human bnc1 (NP_001708.3), of the Drosophila disco (NP_523362.2) and discorelated (NP_727938.1) proteins and of the unique disco protein of the louse (PED: Pediculus humanus corporis), the flour beetle (TRI: Tribolium castaneum), the honey bee (API: Apis mellifera), and the jewel wasp (NAS: Nasonia vitripennis). The non-Drosophila disco sequences were deduced from genomic sequences identified by similarity searches using the human bnc2 amino acid sequence (Pediculus: AAZO01002822.1 and AAZO01000000, Tribolium: XP_971658.1, Apis: NW_001253429 and Nasonia: NW_001817459.1). The cysteines and histidines of the zinc fingers are in bold type and underlined. Conservative amino acid replacements are in blue type. Numbers are relative to the first methionine. (B) Comparison of intron boundaries of bnc2, bnc1, and disco. (C) Structure of the basonuclins and disco proteins. Basonuclins contain 3 pairs of zinc fingers (vertical bars) and an NLS (red dot) located between fingers 2 and 3. Disco proteins contain from 1 to 3 pairs of zinc fingers and an NLS placed as in the basonuclins. NLS predicted with PredictNLS software.