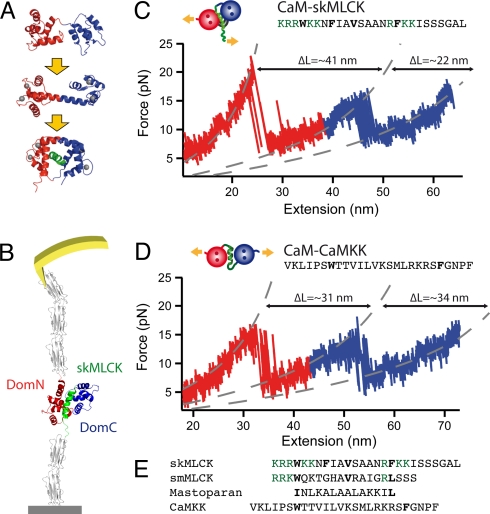
Fig. 1.
(A) Structure of CaM in different ligand binding states. DomN is shown in red, DomC in blue. Upper picture, apo CaM; middle, Ca2+ loaded form, Ca2+ ions are shown in gray; lower picture, Ca2+-CaM bound to target peptide skMLCK (green). (B) Scheme of the experimental setup. CaM-skMLCK is incorporated into filamin domains (gray) that serve as handles for attaching the protein construct to a surface and to an AFM cantilever tip. (C) Typical force vs. extension trace of skMLCK fused to CaM (CaM-skMLCK) at a pulling velocity of vpull = 0.5 nm/s. Unfolding peaks of DomN and DomC of CaM-skMLCK are shown in red and blue, respectively. WLC curves are shown in gray. In the skMLCK amino acid sequence, hydrophobic anchor residues are highlighted in bold type, charged amino acids directly adjacent to these hydrophobic residues are colored in green. (D) Force vs. extension trace of CaMKK inserted between DomN and DomC of CaM (CaM-CaMKK), recorded at a pulling velocity of 1 nm/s. Again, unfolding peaks of DomN and DomC of CaM-skMLCK are shown in red and blue, respectively. (E) Sequence alignment of the target peptides skMLCK, smMLCK, mastoparan, and CaMKK. Hydrophobic anchor residues are shown in bold font, and charged amino acids directly adjacent to hydrophobic anchor residues are colored in green.