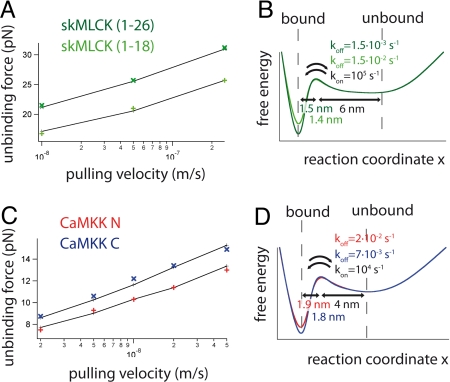
Fig. 5.
(A) Pulling speed dependence of mean unbinding force (first peak of the trace) of skMLCK (1–26; dark green) and skMLCK (1–18; light green) at nonequilibrium conditions. Results of Monte Carlo simulations are shown in black. (B) Calculated potential energy landscape at zero force for binding/unbinding of skMLCK (1–26) and skMLCK (1–18) to CaM. (C) Unbinding forces vs. pulling speed are shown for CaMKK N (first peak in Fig. 3E) and CaMKK C (third peak in Fig. 3E) in red and blue, respectively. Since equilibrium conditions prevail at low pulling velocities, forces of the first unbinding transition were analyzed. Results of Monte Carlo simulations are shown in black. (D) Calculated potential energy landscape at zero force for binding/unbinding of CaMKK N and CaMKK C.