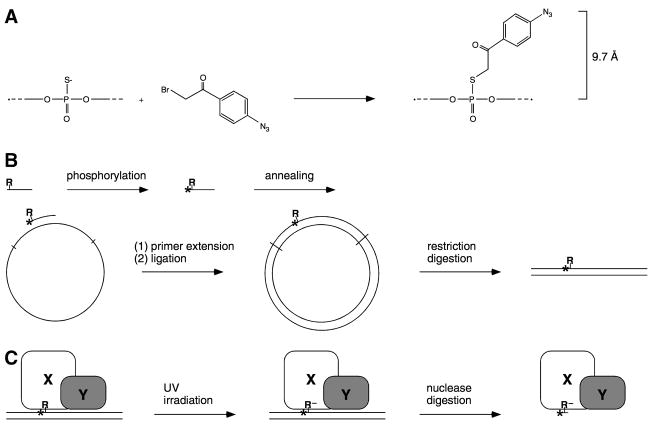
Figure 1.
Site-specific protein-DNA photocrosslinking (1–6). (A,B) Chemical and enzymatic reactions are used to prepare a full-length-promoter DNA fragment with a phenyl-azide photoactivatible crosslinking agent (R) and an adjacent radioactive phosphorus (*) incorporated at a single, defined site. Based on the chemistry of incorporation, the maximum distance between the site of incorporation and the photoreactive atom is 9.7 Å; the maximum distance between the site of incorporation and a crosslinked atom is ~11 Å. (C) UV-irradiation of the derivatized protein-DNA complex initiates crosslinking. Nuclease digestion eliminates uncrosslinked DNA and converts crosslinked, radiolabelled DNA to a crosslinked, radiolabelled 3–5 nucleotide “tag.”