Figure 2.
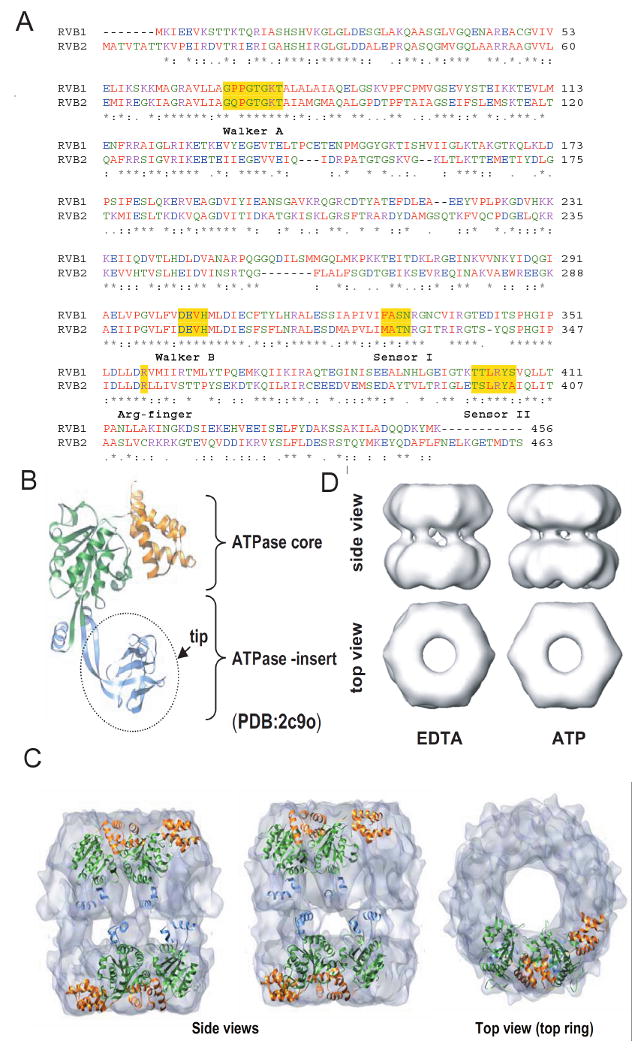
Sequence and structural details of RVBs. (A) Protein sequence alignment of human RVB1 and RVB2 showing regions of similarity where Walker A, Walker B, sensor 1, sensor 2 and arginine finger are highlighted. (B) Structure of monomeric RVB1. ATPase core domain consisting of domain I (1-120 aa + 296-365 aa) and domain III (368-456 aa) and ATPase insert domain II (121-295 aa) are shown. (C) Electron microscopic (EM) image of dodecameric RVB1 and RVB2. RVB1 and RVB2 are arranged as a double hexamer and interact through their ATPase insert domain. (D) Change in conformation after binding of ATP. Different views of the EM images of RVB1 and RVB2 in presence of ATP or EDTA.
