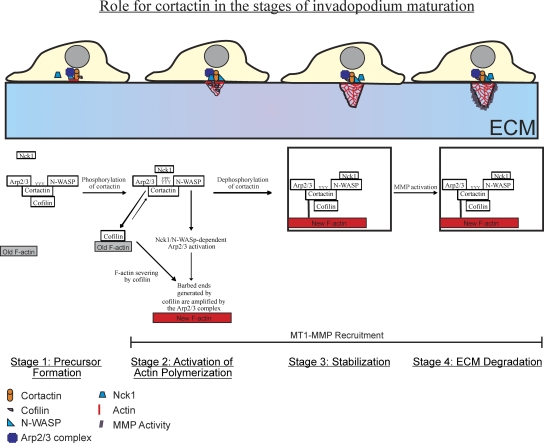
Figure 9.
Cortactin regulates the activities of cofilin and N-WASp to control the stages of invadopodium assembly and maturation (model). During precursor formation (stage 1), cortactin, N-WASp, cofilin, and Arp2/3 form a complex involving cortactin's Arp2/3 and N-WASp binding domains. Cortactin is then tyrosine phosphorylated, which activates cofilin's severing activity to generate free barbed ends and the Arp2/3 complex can use these cofilin-generated barbed ends for efficient actin polymerization (stage 2). Cortactin is then dephosphorylated, which stabilizes the invadopodium precursor for maturation (stage 3). Box at stage 3 and 4 indicates stabilization. MT1-MMP can be recruited at stages 2–4. Stages 1–3 are required for a precursor to become a mature invadopodium that efficienctly degrades ECM (stage 4).