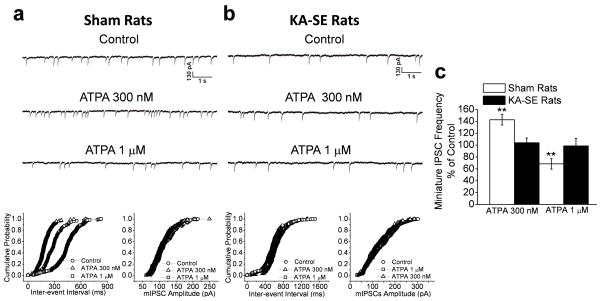
Figure 7. The GluK1R-mediated effects on presynaptic GABA release in the BLA are nearly absent after KA-SE.
In the sham control group, the GluK1R agonist ATPA, at 300 nM, increased the frequency of mIPSCs recorded from BLA pyramidal neurons (a1); this effect was almost absent in the KA-SE rats (b1). At 1 μM, ATPA reduced the frequency of mIPSCs in the sham group (a1), but, again, had virtually no effect in the KA-SE group (b1). Cumulative probability plots of interevent intervals and amplitudes of mIPSCs corresponding to the traces in a1 and b1 are shown in a2 and b2, respectively. (c) Pooled mIPSC frequency-data of 9 slices from KA-SE rats and 9 slices from sham rats expressed as a percentage of the mIPSC frequency during control conditions (before application of ATPA); **p< 0.01.