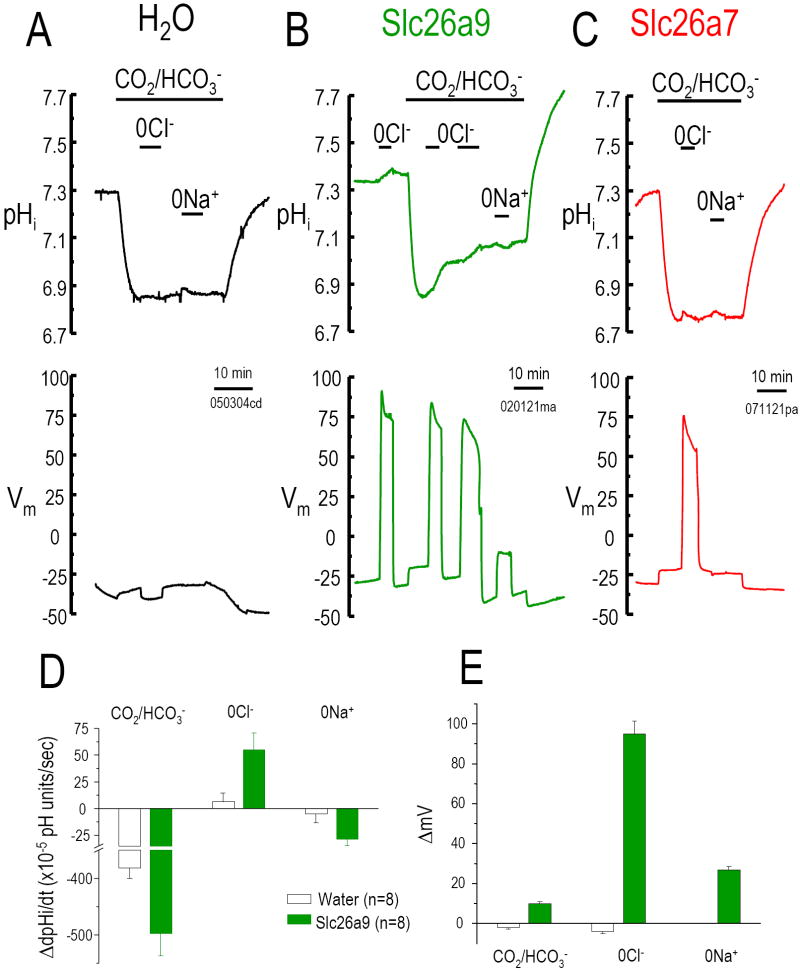
Fig 3. Cl--HCO3- exchange activity.
Intracellular pH (pHi) and membrane potential (Vm) changes of water injected Xenopus oocyte (A) and oocytes expressing Slc26a9 (B) or Slc26a7 (C) are measured using microelectrodes (see Methods). Bath Cl- removal (0Cl-, gluconate replacement) in the presence of 5% CO2/ 33 mM HCO3- (pH 7.5) will increase pHi as Cl- moves out of the oocyte in exchange for HCO3- (moving into oocyte). Na+ removal (in CO2/HCO3-) is an indication of Na+/HCO3- cotransporter activity (Na+ and HCO3- moving out of the oocyte together). 0Cl- elicits a pHi increase (base loading) in Slc26a9 (B) cells but not Slc26a7 (C). 0Cl- also elicits a Vm increase for both Slc26a9 and Slc26a7. Averaged pHi change rates (10-5 pH units/sec) and membrane potential changes (ΔmV) due to addition of CO2/HCO3-, Cl- removal, and Na+ removal are shown in D and E, respectively.