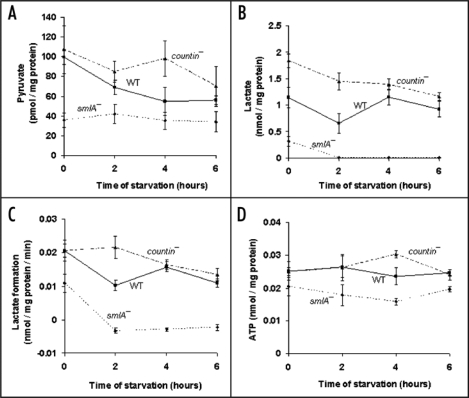
Figure 1.
Cells with different levels of extracellular CF have different levels of pyruvate, lactate, lactate formation in lysates, and ATP. countin−, wild-type (WT) and smlA− cells were starved by shaking in PBM, harvested at the times indicated, and the levels of metabolites were measured in the three cell lines. (A) Pyruvate levels. At 0 hours, the differences between smlA− and WT cells, and between smlA− and countin− cells were significant. At 2 hours of starvation, the difference between smlA− and countin− cells was significant. In addition, a t-test indicated that the difference at 4 hours between smlA− and countin− cells was significant. Values are means ± SEM from at least 4 independent assays. (B) Lactate levels. The measured values of lactate in smlA− cells at 2, 4 and 6 hours of starvation were 8.9 ± 7.7, 5.9 ± 6.0 and 9.7 ± 8.4 pmol/mg protein, respectively. At 0 and 2 hours, the differences between smlA− and WT, WT and countin−, and smlA− and countin− cells were significant. At 4 and 6 hours of starvation, the differences between smlA− and WT, and smlA− and countin− cells were significant. Values are means ± SEM from at least 6 independent assays. (C) The formation of lactate in lysates. The negative values for smlA− at 2, 4 and 6 hours indicate that lactate was used faster than it was made. At 0 hours, the difference between smlA− and WT lysates was significant, and at 2 hours of starvation, the differences between smlA− and WT, WT and countin−, and smlA− and countin− lysates were significant. At 4 and 6 hours of starvation, the differences between smlA− and WT, and smlA− and countin− lysates were significant. Values are means ± SEM from 6 independent assays. (D) ATP levels. At 4 hours of starvation, the differences between smlA− and WT, WT and countin−, and smlA− and countin− cells were significant. At 6 hours of starvation, the differences between smlA− and WT, and smlA− and countin− cells were significant. Values are means ± SEM from five independent assays.