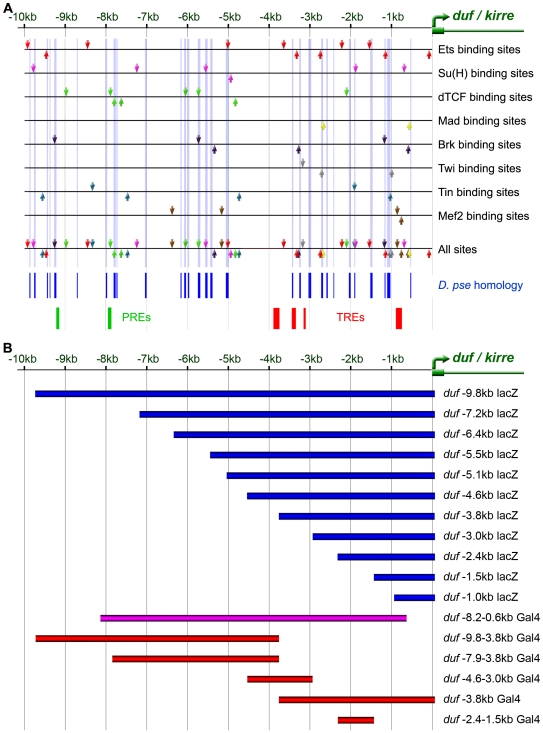
Figure 1. Consensus binding sites in duf enhancer sequences and deletion analysis of duf genomic region.
A. Occurrence of binding sites for nuclear effectors of signaling pathways and mesodermal factors in the 10 kb sequence 5′ to duf is diagrammatically shown. Published consensus binding sequences for Ets, Su(H), Ci, dTCF, Mad, Brk, Twi, Tin, Mef2 are shown. Downward pointing arrow indicates binding on + strand and upward pointing arrow indicates binding on –strand. Sequences that are well conserved in D. pseudoobscura are shown as blue vertical bars. Several putative binding sites for GAGA factor encoded by the Trithorax-like gene (Trl) characteristic of TREs (Trithorax Response Elements) are present within 3.8 kb from the duf start site (red verticle bars) but no sites further upstream in the 10 kb region. Similarly, putative binding sites for PHO (pleiohomeotic) and PHO-like, polycomp group proteins (PcG) that bind to PREs (Polycomb group Response Elements) are found between −8.0 kb to −9.3 kb region (green vertical bars). B. Schematic of constructs generated to characterize the regulatory potential of putative duf enhancer sequences during Drosophila embryonic and adult myogenesis. Putative enhnacer fragments with deletions from both distal (blue bars) and proximal ends (red bars) of the duf 5′ region were PCR amplified and cloned as EcoRI - BamHI fragments into pCaSpeR AUG βGal, or pPTGal. Transgenic flies were generated from these constructs producing either lacZ (blue bars) or Gal4 lines (red bars). duf −8.2−0.6 was cloned into ZGLpWW vector (magenta bar).