Figure 1.
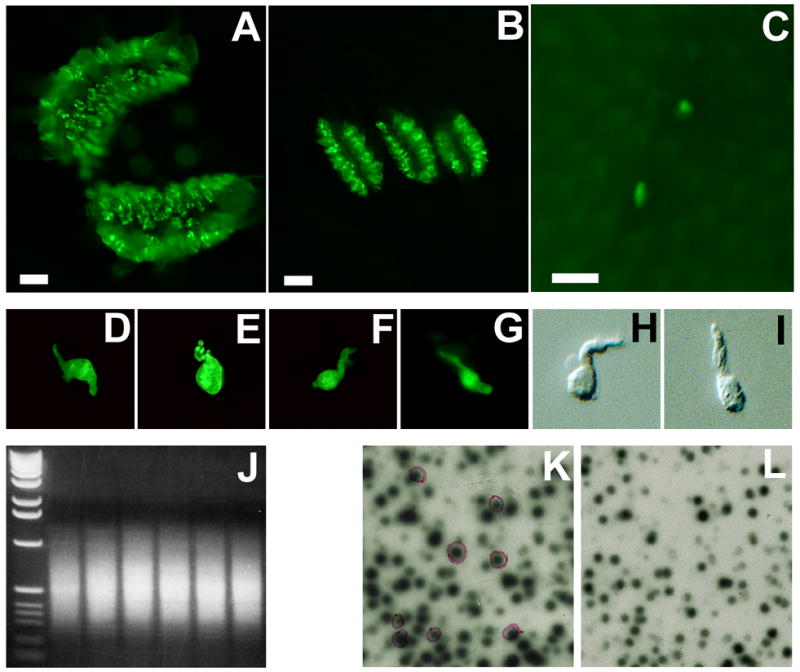
Isolation of taste cell-selective genes. GFP-labeled taste papillae (A: circumvallate; B: foliate; and C: fungiform. Scale bar: 250 μm) were isolated from GFP transgenic mice and dissociated into individual taste bud cells (D to G: four green fluorescent cells; H and I: two non-fluorescent cells). Transcripts from each cell were amplified by PCR with an average size of 600 bp (J: an electrophoretic gel image of amplified products from the six single cells; left lane: 1 kb DNA molecular weight marker). A portion of the amplified products was used to construct single cell cDNA libraries, which were subtractively screened: λ bacteriophage double lift was screened with self-probe (K) and non-taste-probe (L). Differentially expressed clones with stronger signals on the left lift (K) and weaker or no signals on the right lift (L), shown in purple circles, were identified and sequenced.
