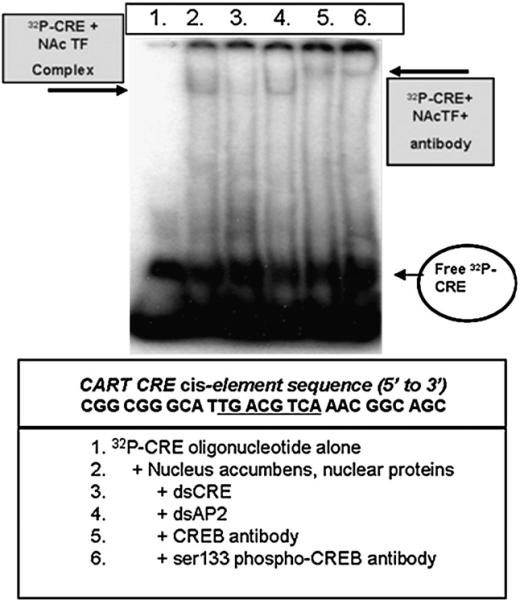
Fig. 1.
Oligonucleotides containing the CART promoter CRE cis-regulatory element bind to CREB and phospho-CREB from the rat NAc. EMSA and super shift analyses were performed using nuclear proteins from the NAc as described in the Experimental procedures (the gel shown is representative of the data from at least five other animals assayed separately in independent experiments). The sequence of the regions of the CART promoter containing the CRE cis-element (the 27mer is referred to as the “CRE”) is given below the picture of the gel in the box, and the core binding sequence is underlined. 32P-CRE+NAc transcription factor (TF) complexes were visualized by incubating proteins extracted from cell nuclei with a 32P-radiolabeled oligonucleotide identical in sequence to the CART gene CRE cis-regulatory element along with its flanking sequence, and separating free 32P-CRE (see figure's bottom right) from the 32P-CRE+NAc TF complex on a polyacrylamide gel (complex is denoted by boxed arrow at the figure's top left). The identity of the protein in the 32P-CRE+NAc TF complex was determined by super shift analysis using either a CREB- or ser133 phospho-CREB-specific antibody (see box at top right denoting the 32P-CRE+NAc TF+antibody complex). See text for additional details.