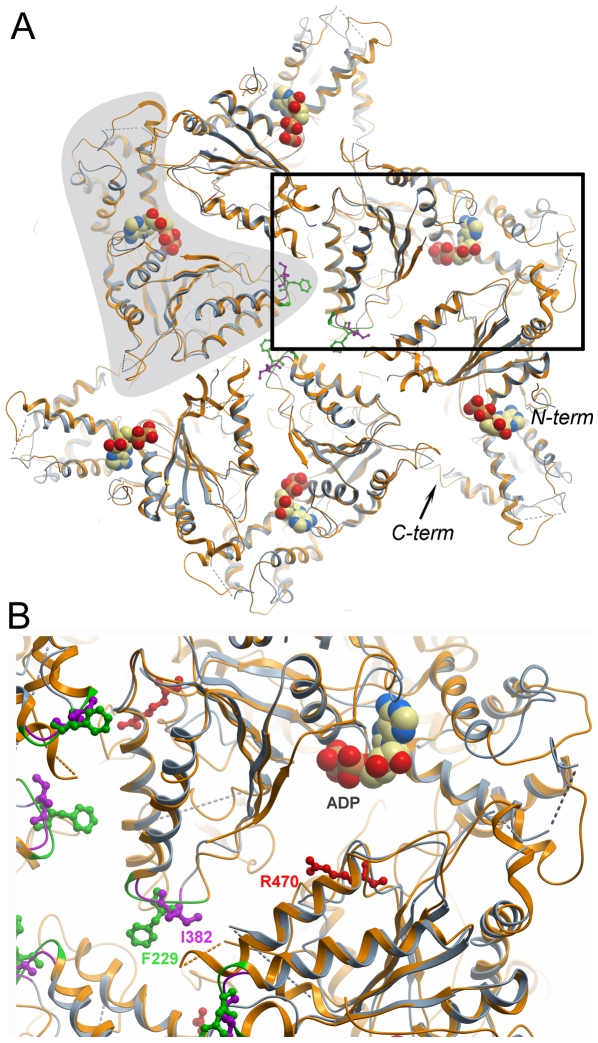
Figure 5. Model of the paraplegin hexamer.
A. The hexameric structure of paraplegin305–565 was modelled by aligning our crystal structure (blue) with each monomer within the T. thermophilus FtsH hexamer crystal structure (2dhr; orange). The outline of one monomer is indicated by grey shading, and the N- and C-termini of another monomer are indicated. The boxed area is expanded in panel B. B. Close-up of the region around the pore loops and the monomer interface around the nucleotide binding site. The hydrophobic pore loop residue Phe228 of FtsH, implicated in substrate binding, is shown in green, and the corresponding paraplegin residue Ile832 is shown in purple. Paraplegin Arg470, shown in red, is a putative arginine finger that activates ATP hydrolysis in the neighbor monomer following a conformational change in the ring structure.