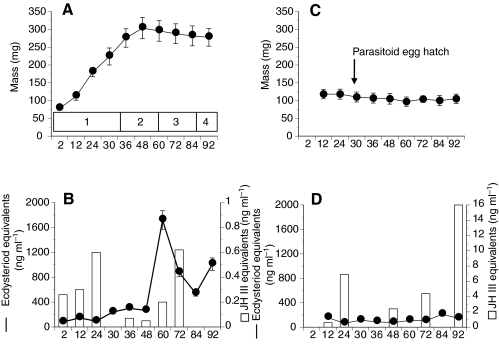
Fig. 1.
Growth, ecdysteroid, and juvenile hormone (JH) titers in normal fifth instar P. includens larvae (A,B) and fifth instars parasitized at 12 h by M. demolitor (C,D). (A) The mean ± s.d. wet mass of P. includens is plotted in relation to time (hours) post-ecdysis and phase of growth as indicated in the box above the x-axis. Stages of growth are: 1, pre-critical weight feeding phase with minimum viable weight being achieved between 24 and 30 h and critical weight being achieved by 36 h; 2, post-critical weight feeding phase; 3, wandering and cocoon-spinning phase; and 4, pupation. (B) Hemolymph ecdysteroid titers are shown as a black line (± s.e.), while JH titers are shown as open bars. (C) The wet mass of parasitized P. includens is plotted in relation to time (hours) post-ecdysis. The timing of hatching of the M. demolitor egg is indicated. (D) ecdysteroid and JH titers are shown as described in B but note the difference in scaling of the y-axis for JH. Sources: staging characters for P. includens (Strand, 1990), hemolymph JH titers in normal and parasitized larvae (Balgopal et al., 1996). Critical sizes and hemolymph ecdysteroid titers were determined during the current study.