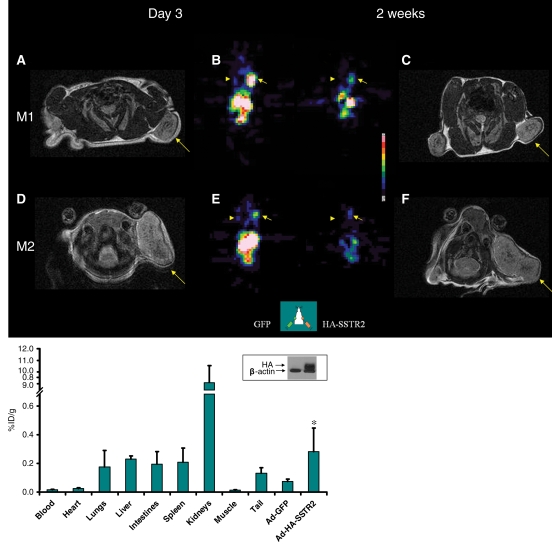
Figure 4:
Longitudinal MR and SPECT imaging data in MDA-MB-435 tumor–bearing mice infected in vivo with Ad-HA-SSTR2. A, D, E, and H, Axial T2-weighted MR images and, B, C, F, and G, SPECT images 3 days (A, B, E, and F) and 2 weeks (C, D, G, and H) after adenoviral infection in two representative mice, M1 (A, B, C, and D) and M2 (E, F, G, and H). MR images are focused on the tumor on the left side to demonstrate tumor size. Tumor size does not correspond with size of the object on the SPECT image. There was variability between animals (M1 vs M2) in change in tumor size, stable in M1 (A vs D, arrow) and increased in M2 (E vs H, arrow), and in amount of uptake at first time point (B vs F, arrow) and second time point (C vs G, arrow). Increased uptake was seen in tumors infected with Ad-HA-SSTR2 (B, C, F, and G, arrow) versus those infected with control Ad-GFP virus (B, C, F, and G, arrowhead). Uptake decreased in tumors infected with Ad-HA-SSTR2 in both mice at the later time point (C vs B and G vs F, arrow). Left tumor was injected with Ad-GFP; right tumor was injected with Ad-HA-SSTR2. Two days later, MR imaging and intravenous injection of 111In-octreotide were performed. The next day, gamma camera imaging was performed. Two weeks later, MR imaging and intravenous injection of 111In-octreotide were performed. The next day, gamma camera imaging was performed. I, Graph of ex vivo biodistribution of 111In-octreotide injected in mice bearing subcutaneous MDA-MB-435 tumors injected in vivo with Ad-HA-SSTR2 or control virus. After the second imaging time point (2 weeks after adenovirus injection), tumors were excised for ex vivo biodistribution analysis. Increased uptake was seen in tumors infected with Ad-HA-SSTR2. Inset: Western blot results in tumors with anti-hemagglutinin A antibody for the expressed HA-SSTR2 fusion protein and with anti-β-actin antibody. * = P = .01, n = 6, t test comparing tumors infected with Ad-HA-SSTR2 versus tumors infected with Ad-GFP. %ID/g = percentage of injected dose per gram. Error bars = standard deviation.