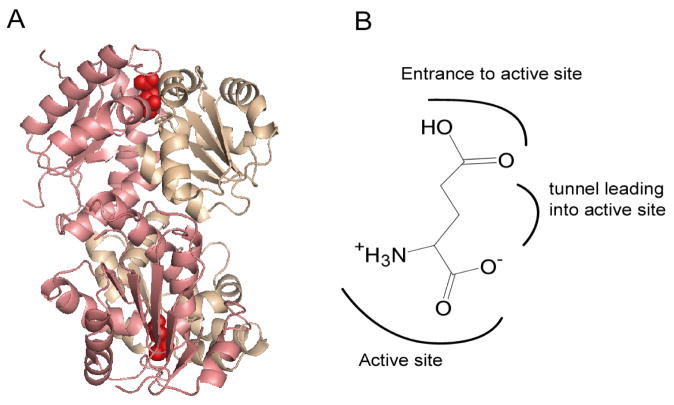
Figure 1.
(A) Crystal structure of RacE2. The two domains in each monomer in the dimer are shaded in pink and beige. Domain I (pink) consists of residues 1–95, and 208–270, which form five α-helices encircling a six-stranded parallel β-sheet. Domain II (beige) includes residues 96–207 and is comprised of six α-helices surrounding a four stranded parallel β-sheet. The active site is on the face opposite the dimer interface and is indicated by the presence of D-Glu (red). This figure was generated by PyMOL. (B) Orientation of D-Glu in the active site of RacE2 as seen in the crystal structure, with the α-groups centered in the active site, and the side chain pointing away from the catalytic residues.