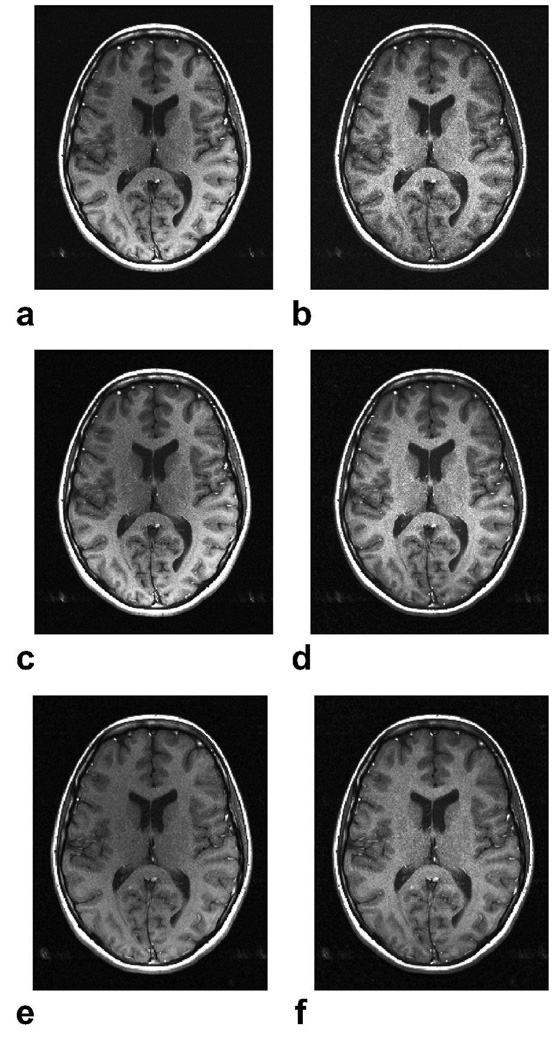
Figure 5.
In vivo brain images were acquired with a spin-echo sequence and an 8-channel head coil with the following parameters: α = 90°, TR = 300 ms, 24 cm FOV, 0.7 × 0.7 × 4 mm3, 31.25 kHz bandwidth, and a total of 10 slices collected within 1:43 min. a: Psos, b: Pnorm, c: Popt (p = 2), d: Popt (p = 0.5). The Psos and Popt (p = 2) images achieve high SNR, but have coil sensitivity related amplitude modulations that affect the image contrast. On the other hand, the Pnorm method significantly increases the signal homogeneity at the expense of reduced SNR. The Popt (p = 0.5) combination both improves homogeneity and achieves near-optimal SNR as seen in d. Two-fold undersampled brain images were acquired with the same parameters, except for 1 mm in-plane resolution. The central 1/16th portion of k-space was fully sampled for calibration purposes. The SENSE reconstructions for p = 2 (e) and p = 0.5 (f) are shown. The signal homogeneity is enhanced with p = 0.5.