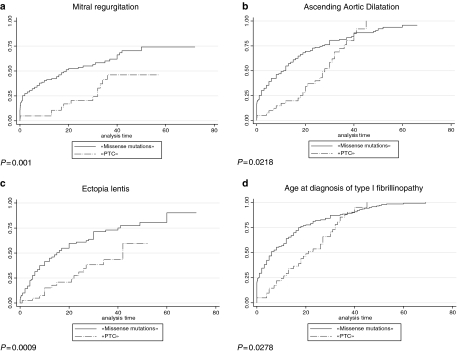
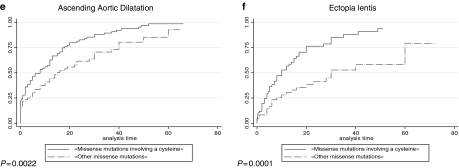
Figure 5.
Kaplan–Meier analyses for various clinical features in patients with a missense mutation in exons 24–32 compared to patients with a premature termination codon (PTC) mutation in the same region. (a) Probability of mitral insufficiency in missense mutations in exons 24–32 versus PTC mutations in the same region. The cumulative probability of mitral insufficiency diagnosed before or at 25 years was 54% (99.9% CI=39–69%) in patients with a missense mutation in exons 24–32 (solid line) compared to 20% (99.9% CI=5–53%) in patients with a PTC mutation in the same region (broken line) (P=0.001). (b) Probability of ascending aortic dilatation in missense mutations in exons 24–32 versus PTC mutations in the same region. The cumulative probability of ascending aortic dilatation before or at 25 years was 74% (99.9% CI=60–86%) in patients with a missense mutation in exons 24–32 (solid line) compared to 40% (99.9% CI=18–70%) in patients with a PTC mutation in the same region (broken line), but these results were not significant because the curves join together with follow-up (P=0.0218). (c) Probability of ectopia lentis in missense mutations in exons 24–32 versus PTC mutations in the same region. The cumulative probability of ectopia lentis diagnosed before or at 25 years was 61% (99.9% CI=45–77%) in patients with a missense mutation in exons 24–32 (solid line) compared to 31% (99.9% CI=11–63%) in patients with a PTC mutation in the same region (broken line) (P=0.0009). (d) Age at diagnosis of type I fibrillinopathy in missense mutations in exons 24–32 versus PTC mutations in the same region. Fifty-five percent of patients with a missense mutation in exons 24–32 (solid line) were diagnosed at 6 years (IQR (0.7;18)) of age versus 21 years (IQR (11;32)) of age in patients with a PTC mutation in the same region (broken line), but results of the log-rank test were not significant because the curves join together with follow-up (P=0.0278). (e) Probability of ascending aortic dilatation in missense mutations involving a cysteine in exons 24–32 versus other missense mutations in the same region. The cumulative probability of ascending aortic dilatation before or at 25 years was 83% (99.9% CI=70–92%) in patients with a missense mutation involving a cysteine in exons 24–32 (solid line) compared to 62% (99.9% CI=45–78%) in patients with another missense mutation in the same region (broken line), but these results were only marginally significant (P=0.0022). (f) Probability of ectopia lentis in missense mutations involving a cysteine in exons 24–32 versus other missense mutations in the same region. The cumulative probability of ectopia lentis diagnosed before or at 25 years was 76% (99.9% CI=60–89%) in patients with a missense mutation involving a cysteine in exons 24–32 (solid line) compared to 41% (99.9% CI=25–63%) in patients with another missense mutation in the same region (broken line) (P=0.0001).