Fig. 2.
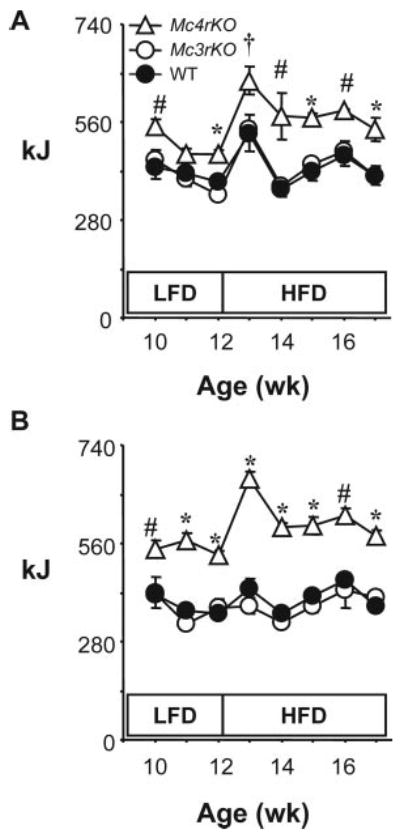
Genotype-specific effects of dietary fat content on food intake of Mc3rKO and Mc4rKO. Weekly food intake (kJ) for male (A) and female (B) WT, Mc3rKO, and Mc4rKO. The legend for this figure is the same as that for Fig. 1, A–D. Food intake was measured during the period indicated by a black bar in Fig. 1, A and B. For each week, significant differences (P < 0.05) are indicated as follows: *, Mc4rKO vs. Mc3rKO, WT; #, Mc4rKO vs. WT; †, Mc4rKO vs. Mc3rKO. Results of two-way ANOVA with repeated-measures analysis examining the effects of diet and genotype for mean weekly intake on low-fat diet (LFD, 10% kJ from fat) and high-fat diet (HFD, 60% kj from fat) are reported in Table 1. Food intake in kilojoules of Mc4rKO, but not Mc3rKO, is increased compared with WT controls, irrespective of diet. Male and female Mc4rKO also increased kilojoules of food consumed when exposed to the high-fat diet. Male WT and Mc3rKO exhibited a transient hyperphagia on the high-fat diet, whereas for female WT and Mc3rKO, kilojoules consumed was not affected by diet.
