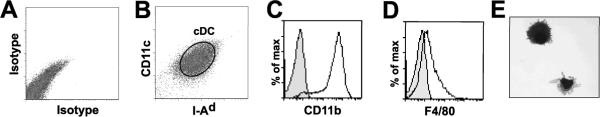
Figure 1.
DC isolation identifies the presence of cDC within the lungs of mice infected with C. neoformans. Lungs from CCR2+/+ mice (14 days post-infection) were lavaged (to remove alveolar macrophages) and enzymatically digested. The resultant single cell suspension of mononuclear cells was cultured (1 hr) on tissue culture plates to further deplete macrophages (by adherence). The non-adherent cells were incubated with CD11c-coated magnetic beads to isolate CD11c positive cells. This population (A–E) was stained with mAbs to either isotype controls (A) or (B) MHC Class II (I-Ad, FITC) and CD11c (allophycocyanin) (representative scatter plots without prior gating). cDC (circular gate labeled cDC) were identified as MHC Class II (I-Ad)+ and CD11c+cells which expressed (C) CD11b and (D) low amounts of F4/80 (representative histograms, open histograms represents Ab specific staining, shaded histograms represents isotype control.). (E) Hematoxylin-eosin staining of these cells confirms a DC morphology with a lobulated nucleus and multiple, fine, cytoplasmic extensions.