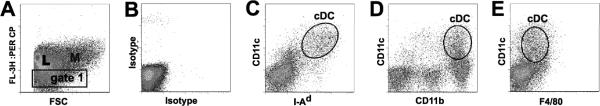
Figure 2.
A flow cytometric analysis strategy identifies cDC amongst total lung leukocytes in the lungs of mice infected with C. neoformans. (A–E) A strategy was devised to identify cDC from bulk mononuclear cell populations obtained from CCR2+/+ mice infected with C. neoformans. Lungs were removed (without lavage) 14 days post-infection and a single cell suspension of all mononuclear cells from enzyme-digested lung mince was obtained. All cells were stained with mAbs to CD3 and CD19 (PerCpCy5.5) to generate an initial plot of FL-3 vs. FSC (A) which identified three cell populations: Lymphocytes (L), small cells which stained for either CD3 or CD19 (PerCpCy5.5); Macrophages (M), large auto-fluorescent cells; and mononuclear cells within Gate 1 (which contained a variety of cell types including cDC). Cells within Gate 1 (B–E) were assessed with the following Ab combinations: (B) isotype controls, (C) MHC Class II (I-Ad, FITC) and CD11c (allophycocyanin); (D) CD11b (PE) and CD11c (allophycocyanin), or (E) F4/80 (PE) and CD11c (allophycocyanin). cDC were identified (C–E) as CD11c+ cells co-expressing MHC Class II (I-Ad), CD11b, and low amounts of F4/80 (representative scatter plots, circular gates labeled cDC).