Figure 4. Metal ion-induced cleavage in the compact versus the native D135 ribozyme.
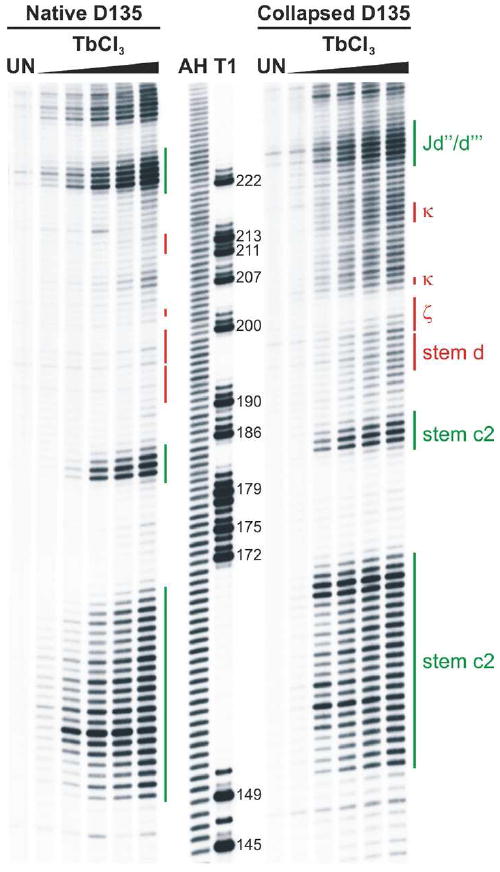
The left panel shows the Tb3+-induced cleavage pattern observed for the native D135 ribozyme and the right panel displays that of the collapsed D135 ribozyme. Lanes designated as UN show background degradation of the labeled RNA. The T1 lane marks the guanosine sequencing lane, while lane AH is the alkaline hydrolysis ladder. Bars on the side of each gel span residues part of a particular structural element, which is also identified on the right panel, whereby the D5 docking site is marked in red and other elements are labeled in green.
