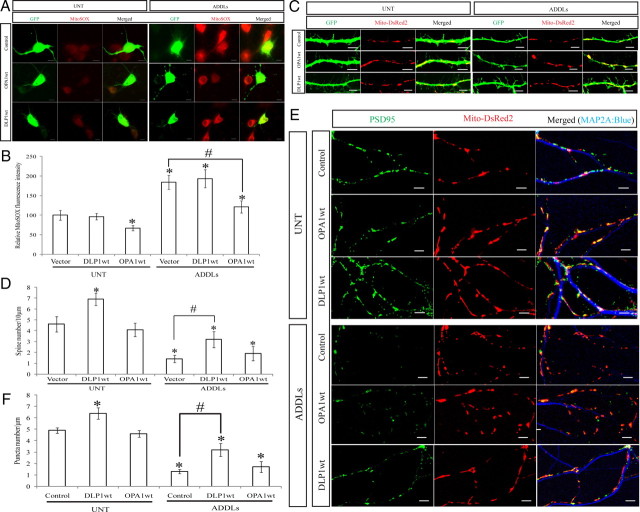
Figure 10.
Effects of DLP1 and OPA1 on ADDL-induced changes in mitochondrial function and neuronal function. A, B, Representative fluorescent pictures and quantification of mitochondrial ROS in neurons (DIV 12) transfected with GFP-tagged wild-type DLP1 or wild-type OPA1 with or without ADDL treatment. Mitochondrial ROS was labeled by MitoSOX; Positive transfected cells were selected by GFP signal. C, D, Representative pictures and quantification of dendritic spine in neurons with or without ADDL treatment. Neurons (DIV 9) were cotransfected with GFP- and Myc-tagged wild-type DLP1 or OPA1. Positive transfected cells were selected on the basis of GFP and Myc staining. E, F, To study the effect of Aβ on PSD-95, neurons (DIV 9) were cotransfected with YFP-tagged PSD-95 to label excitatory synapses, Mito-DsRed2 to label mitochondria, and Myc-tagged DLP1 or OPA1 constructs. Shown are representative pictures and quantification of PSD-95 puncta in neurons with or without ADDL treatment and manipulation. Red, DsRed; green, YFP; blue, MAP2A. Scale bars, 5 μm. At least 20 neurons were analyzed in three independent experiments (*p < 0.05, when compared with the nontransfected or empty vector-transfected normal control cells; #p < 0.05, when compared with control or empty vector-transfected cells with ADDL treatment; Student's t test).