Figure 7. Autoradiography of total and cytisine resistant [125I]epibatidine and [125I]bungarotoxin sites.
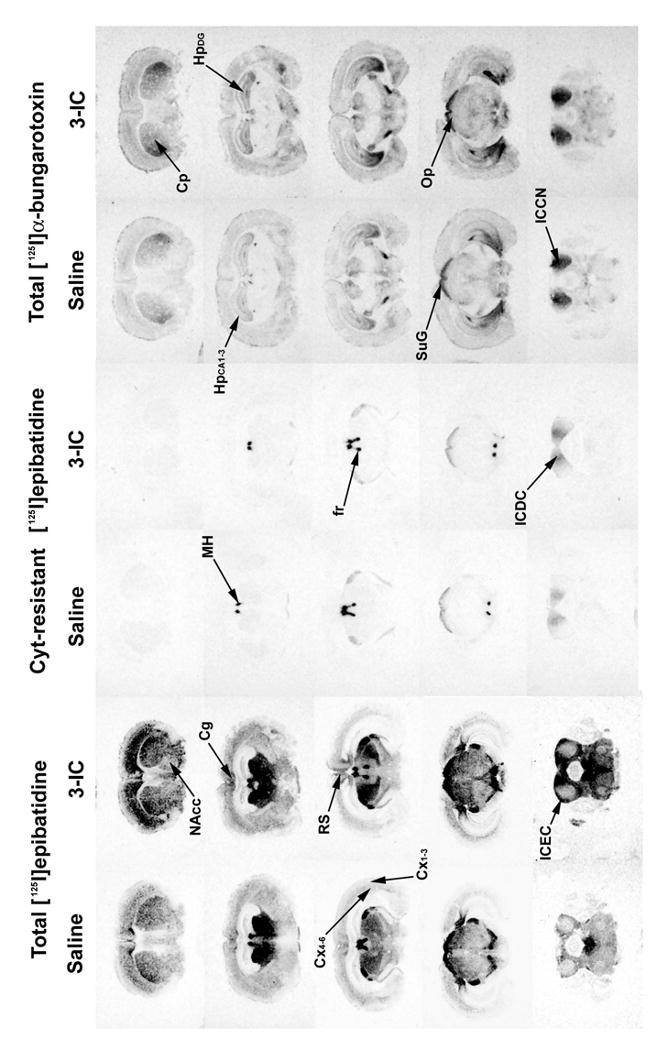
Mice were chronically intravenously infused with 3-IC 0.2 mg/kg/h for 7 days. After treatment, the brains were removed and frozen and coronal sections (14 μm) were obtained and incubated with 1 nM [125I]α-bungarotoxin or 200 pM [125I]epibatidine in presence or absence of cytisine 50 nM. Non-specific binding was determined by adding 1 mM nicotine for [125I]α-bungarotoxin and 100 μM for [125I]epibatidine. Abbreviations: cingulated cortex (Cg), parietal cortex at superficial layers (Cx1-3) and deep layers (Cx4-6), retrosplenial cortex (RS), hippocampus at CA1/CA2/CA3 (HpCA1-3) region and dentate gyrus granule layer (HpDG), caudate putamen (Cp), nucleus accumbens (NAcc), medial habenula (MH), inferior colliculi at dorsal cortex (DCIC), central nucleus (ICCN) and external cortex (ICEC), superior colliculi at superficial gray (SuG) and optic nerve (Op), fasciculus retroflexus (fr).
