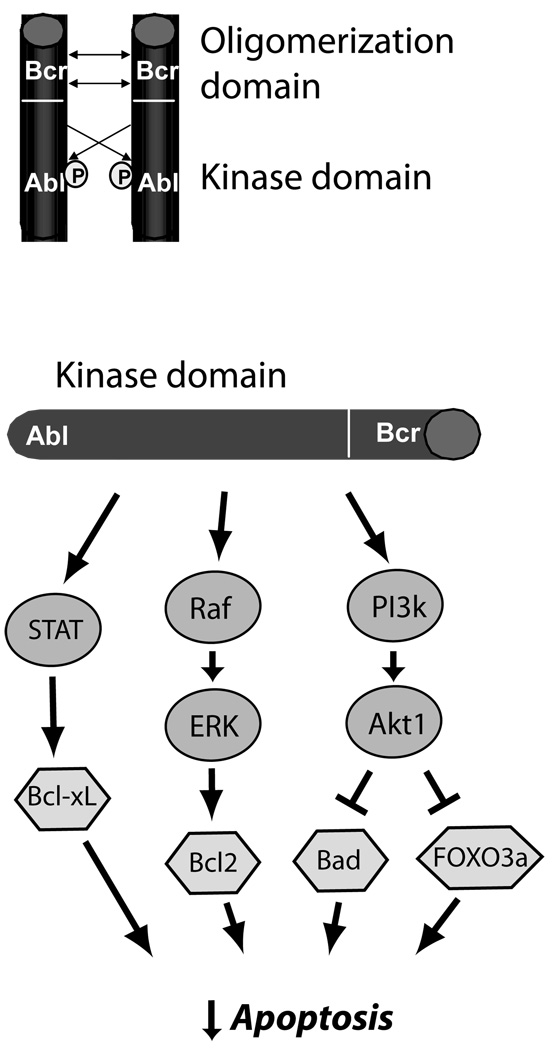
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of carcinogenesis of Bcr-Abl in CML. Oligomerization and cross-phosphorylation (P) of Bcr-Abl fusion proteins (top) leads to constitutive activation of the Abl kinase domain. This leads (bottom) to activation of three key pro-survival pathways, STAT5 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 5), which leads to increased expression of anti-apoptotic Bcl-xL, the Raf → ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinase, or MAP kinase) pathway, which increases expression of anti-apoptotic Bcl2, and the phosphoinositide-3 kinase → Akt pathway, a major anti-apoptotic pathway in cancer cells and cardiomyocytes, that inhibits pro-apoptotic factors FOXO3a and Bad. This culminates in potent inhibition of apoptosis in CML cells.12