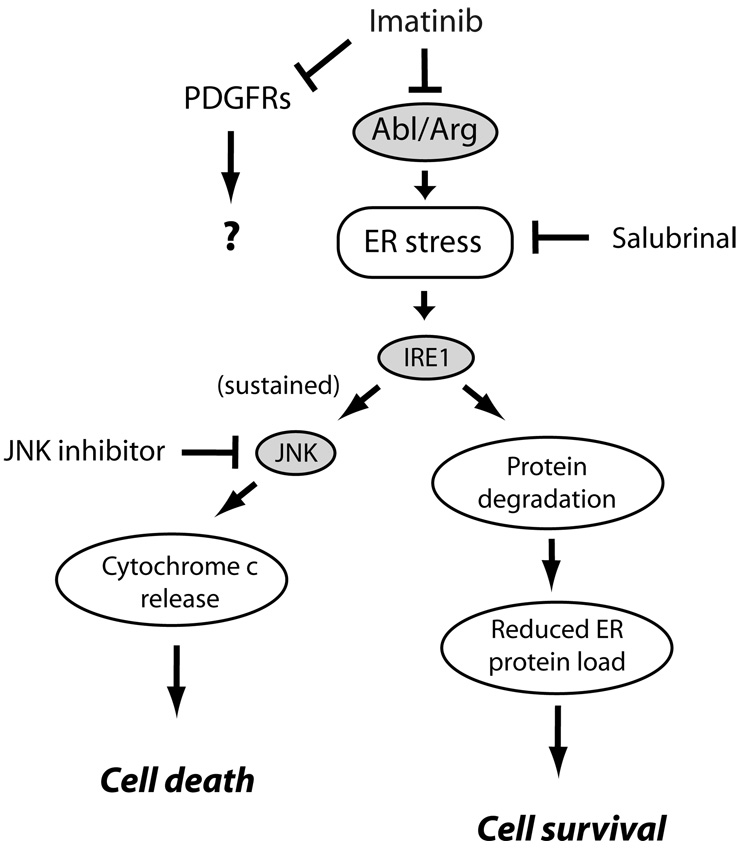
Figure 4.
Pathways of imatinib-induced cardiomyocyte toxicity. Imatinib, via inhibition of Abl/Arg, leads via unclear mechanisms to induction of ER stress. This activates protein kinase IRE1 which upregulates factors involved in degradation of mis-folded proteins in the ER, thereby attempting to restore homeostasis.56 If ER stress is sustained, however, JNKs are activated leading to activation of the intrinsic apoptosis program and cell death. Both salubrinal, an inhibitor of ER stress57, and JNK inhibition by a peptide antagonist, protected from imatinib cardiomyocyte toxicity. The role, if any, of inhibition of PDGFRs in imatinib-induced cardiotoxicity is unknown at this time.