FIG. 6.
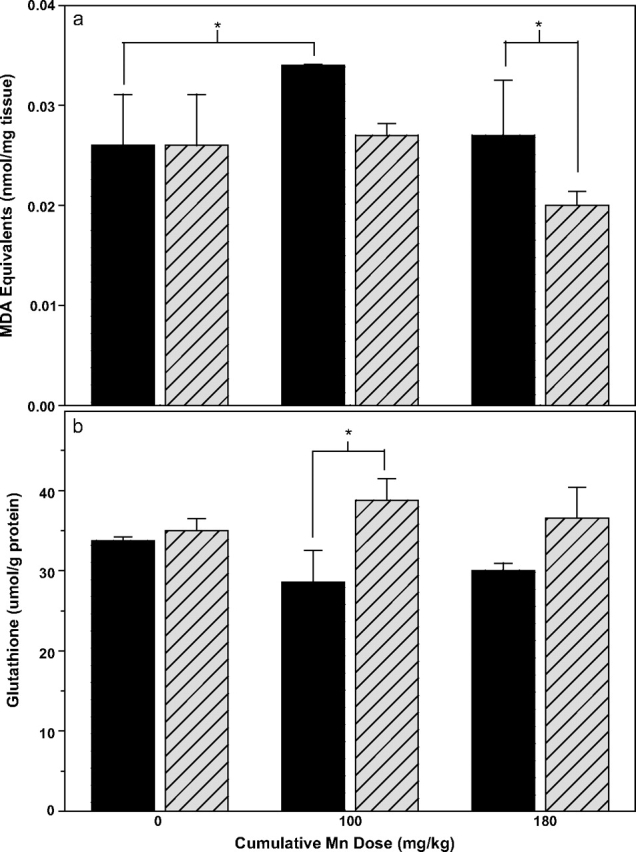
Lipid oxidation (a) and total (oxidized + reduced) glutathione levels (b) in cerebellum of male Cp+/+ (solid bars) and Cp−/− mice (hatched bars) after 4 weeks of manganese treatment (cumulative manganese doses shown on x-axis; mean ± SE, n = 3–4). (a) Two-way ANOVA analysis shows significant manganese treatment (p < 0.05) and ceruloplasmin genotype effects in lipid oxidation (p < 0.05), with a significant difference between genotypes for the 180 mg Mn/kg dose, and a significant difference between the 0 and 90 mg Mn/kg treatment groups for Cp+/+ mice (*p < 0.05, Fisher LSD post hoc test applied to Mn treatments within genotypes and to genotypes within Mn treatments). (b) Two-way ANOVA analysis shows a significant overall genotype effect (p < 0.05), but not an overall manganese treatment effect (p = 0.92). There was a significant difference between genotypes within the 90 mg Mn/kg treatment group (p < 0.05, Fisher LSD post hoc test).
