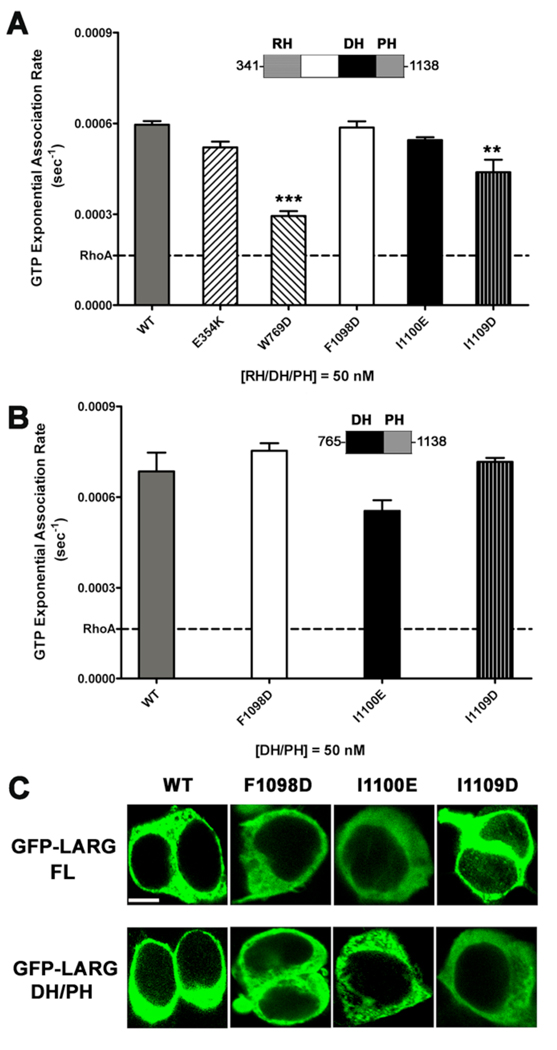
Figure 4. Hydrophobic patch mutations of LARG do not affect activity in vitro nor localization in cells.
(A) GEF activities of RH/DH/PH fragments of LARG. The activity of 50 nM LARG and its mutants were measured as the increase in millipolarization (mP) of BODIPY FL GTPγS upon binding to RhoA in an FP assay. The data from three independent experiments, each measured in triplicate, were fitted with exponential association rates (sec−1), with the error bars giving the SD. W769D had significantly lower activity (***, p<0.001) than WT. The lower activity of I1109D (**, p<0.01) is likely because of its instability (see panel B). (B) GEF activities of LARG DH/PH fragments. The activity of 50 nM WT or hydrophobic patch mutants was measured as in panel (A), and data represents the mean ± SD of two (I1100E and I1109D) or three (WT and F1098D) independent experiments, each measured in triplicate. All three hydrophobic mutants, including DH/PH-I1109D, were not significantly different from WT. (C) Confocal microscopy images of GFP fusions of LARG FL and DH/PH in HEK293T cells. Both FL and DH/PH LARG show diffuse cytoplasmic distribution with no obvious membrane localization. No differences in distribution were observed for the hydrophobic patch mutants. Scale bar: 10 µm.