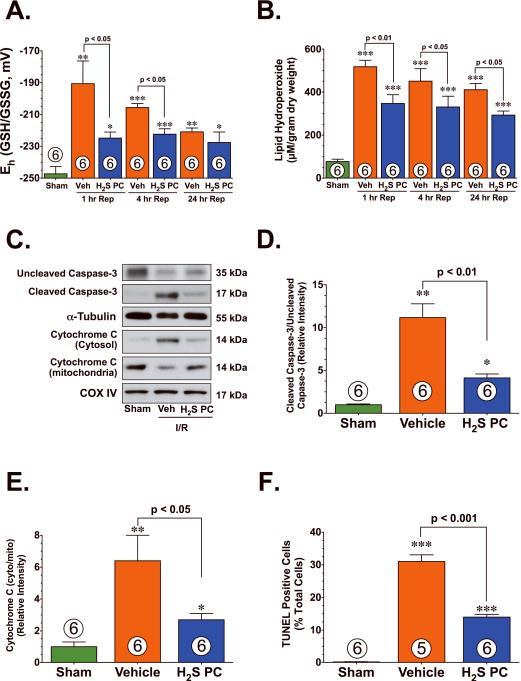
Figure 2.
H2S PC reduced oxidative stress and apoptotic cell death following myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Cardiac (A) redox state (Eh) for GSH and GSSG and (B) lipid hydroperoxide levels (μM) from Sham controls, Vehicle (Veh), and H2S PC treated mice at 1–24 hr of reperfusion following myocardial ischemia. (C) Representative immunoblots of uncleaved caspase-3, cleaved caspase-3, cytosolic cytochrome C, and mitochondrial cytochrome C from the hearts of Sham controls, Veh, and H2S PC treated mice at 4 hr of reperfusion following myocardial ischemia. (D) Ratio of cleaved caspase-3 to uncleaved caspase-3, (E) ratio of cytosolic cytochrome C to mitochondrial cytochrome C, and (F) the number of TUNEL positive cells (% of total nuclei) from the hearts of Sham controls, Veh, and H2S PC treated mice at 4 hr of reperfusion following myocardial ischemia. Values are means ± S.E.M. Numbers inside bars indicate the number of animals that were investigated in each group. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 vs. Sham.